ADHD and Alcohol: Double Diagnosis, Dual Danger, Different Approach Required
Key Takeaways
| Key Takeaways | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Comorbidity Rate | Studies suggest that individuals with ADHD are 2-5 times more likely to develop a substance use disorder, including alcohol use disorder. |
| 2. Risk Factors | Impulsivity, inattention, and hyperactivity in ADHD may contribute to increased risk of alcohol use and abuse. |
| 3. Alcohol Use Patterns | Individuals with ADHD may exhibit earlier onset of drinking, heavier drinking patterns, and increased binge drinking. |
| 4. Brain Chemistry | Alcohol affects brain chemistry, particularly dopamine and serotonin, which are already imbalanced in individuals with ADHD. |
| 5. Medication Interactions | Alcohol can interact with ADHD medications, such as stimulants, reducing their effectiveness or increasing the risk of adverse effects. |
| 6. Increased Risk of Addiction | Individuals with ADHD may be more susceptible to alcohol addiction due to underlying brain chemistry and behavioral factors. |
| 7. Co-occurring Mental Health Conditions | Individuals with ADHD and alcohol use disorder may experience co-occurring mental health conditions, such as depression and anxiety. |
| 8. Treatment Challenges | Treating ADHD and alcohol use disorder simultaneously can be challenging, requiring a comprehensive treatment plan. |
| 9. Importance of Screening | Screening for ADHD and alcohol use disorder is crucial to identify individuals at risk and provide early intervention. |
| 10. Integrated Treatment Approaches | Integrated treatment approaches, including behavioral therapy and medication management, can be effective in addressing both ADHD and alcohol use disorder. |
Introduction to the Relationship Between ADHD and Alcohol Use
The Complex Connection: Understanding the Relationship Between ADHD and Alcohol Use
Individuals with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) are at a higher risk of developing a substance use disorder, particularly concerning ADHD and alcohol. Research suggests that people with ADHD are more likely to engage in excessive drinking and experience negative consequences. This increased vulnerability can be attributed to various factors, including impulsivity, emotional dysregulation, and difficulties with self-regulation, all of which are hallmark symptoms of ADHD.
Studies have shown that individuals with ADHD are more likely to use alcohol as a coping mechanism for their symptoms, intending to self-medicate and alleviating feelings of anxiety, stress, and restlessness. However, this can lead to a vicious cycle of dependence and exacerbate existing ADHD symptoms.
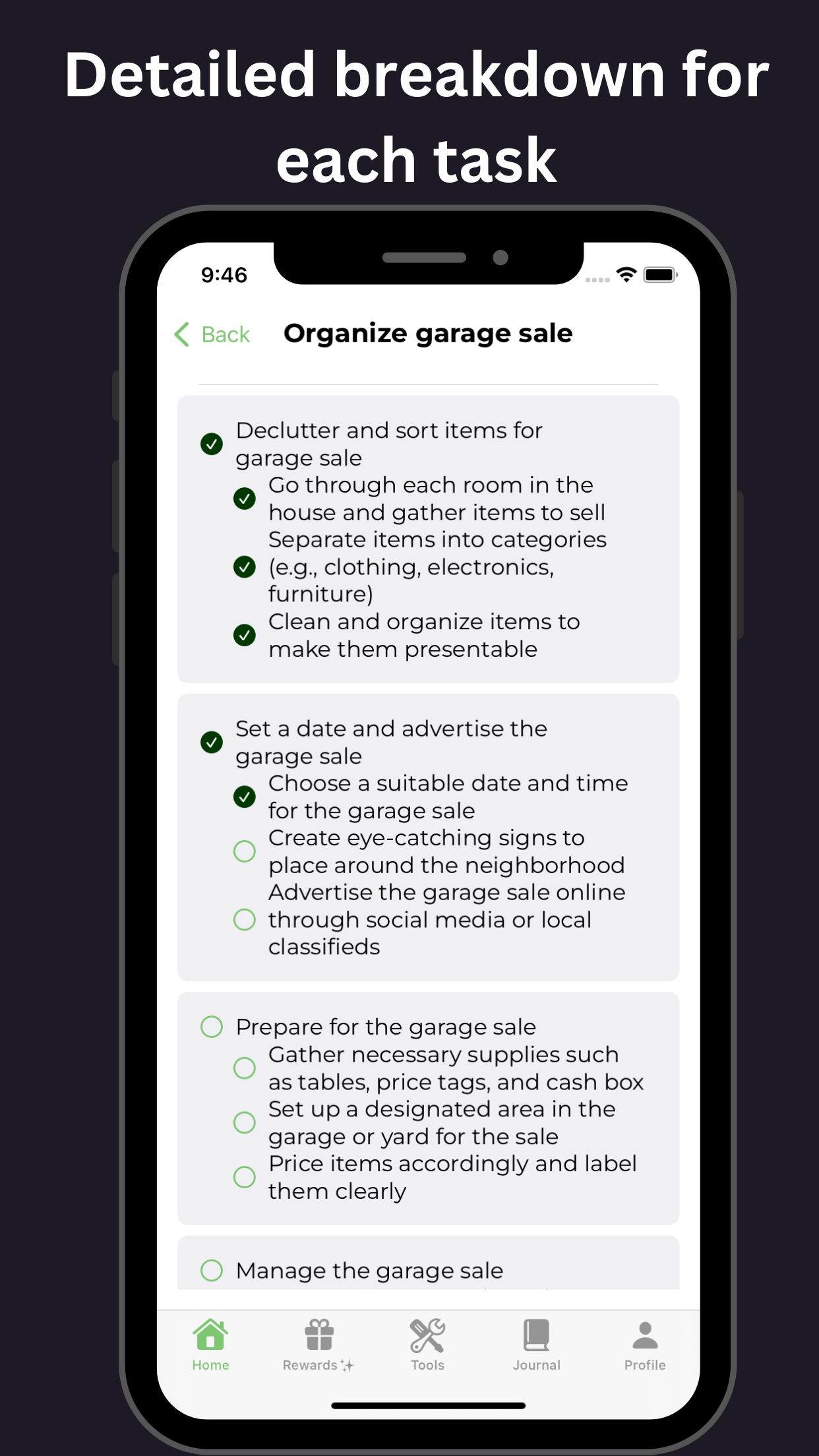
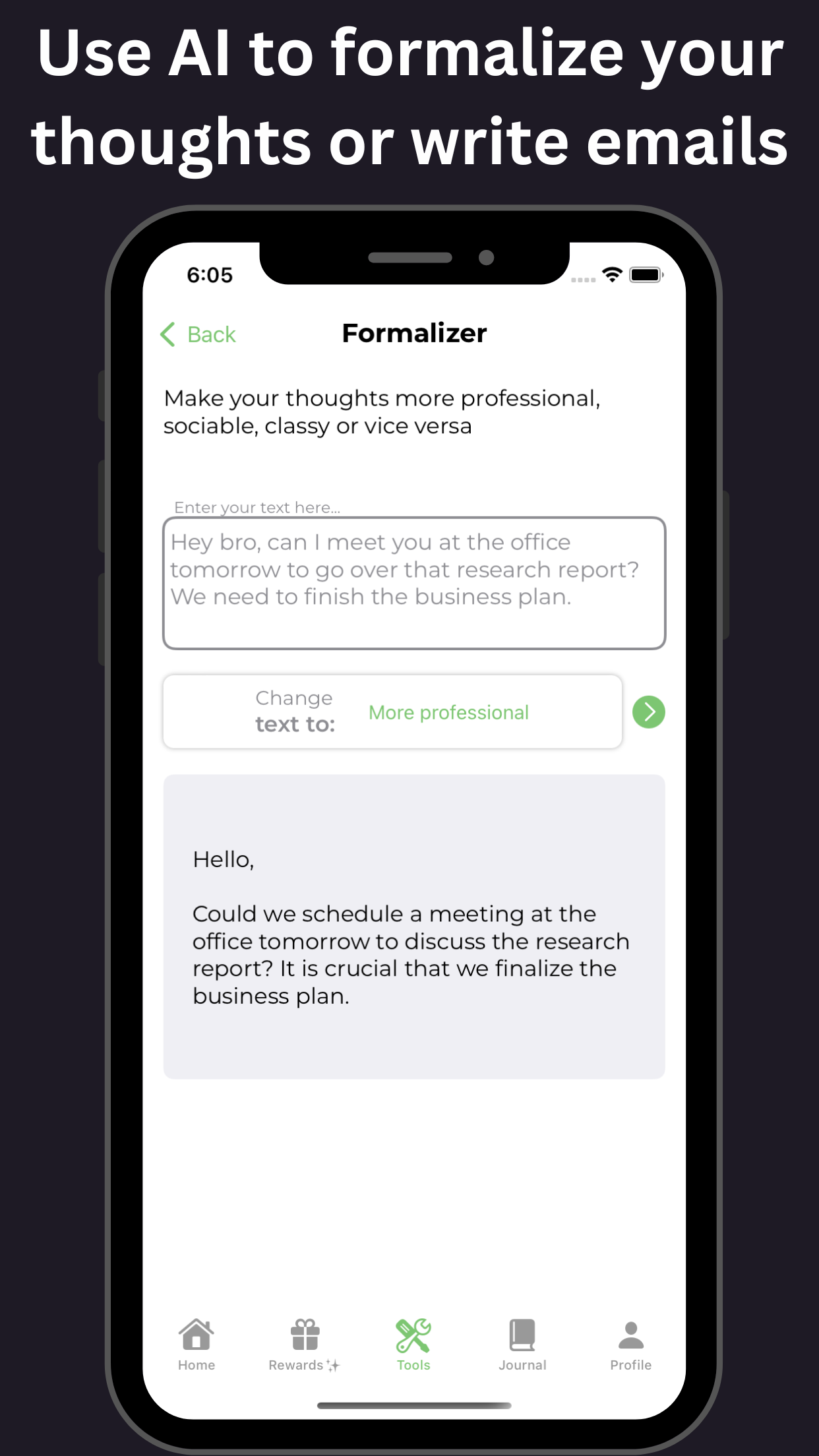
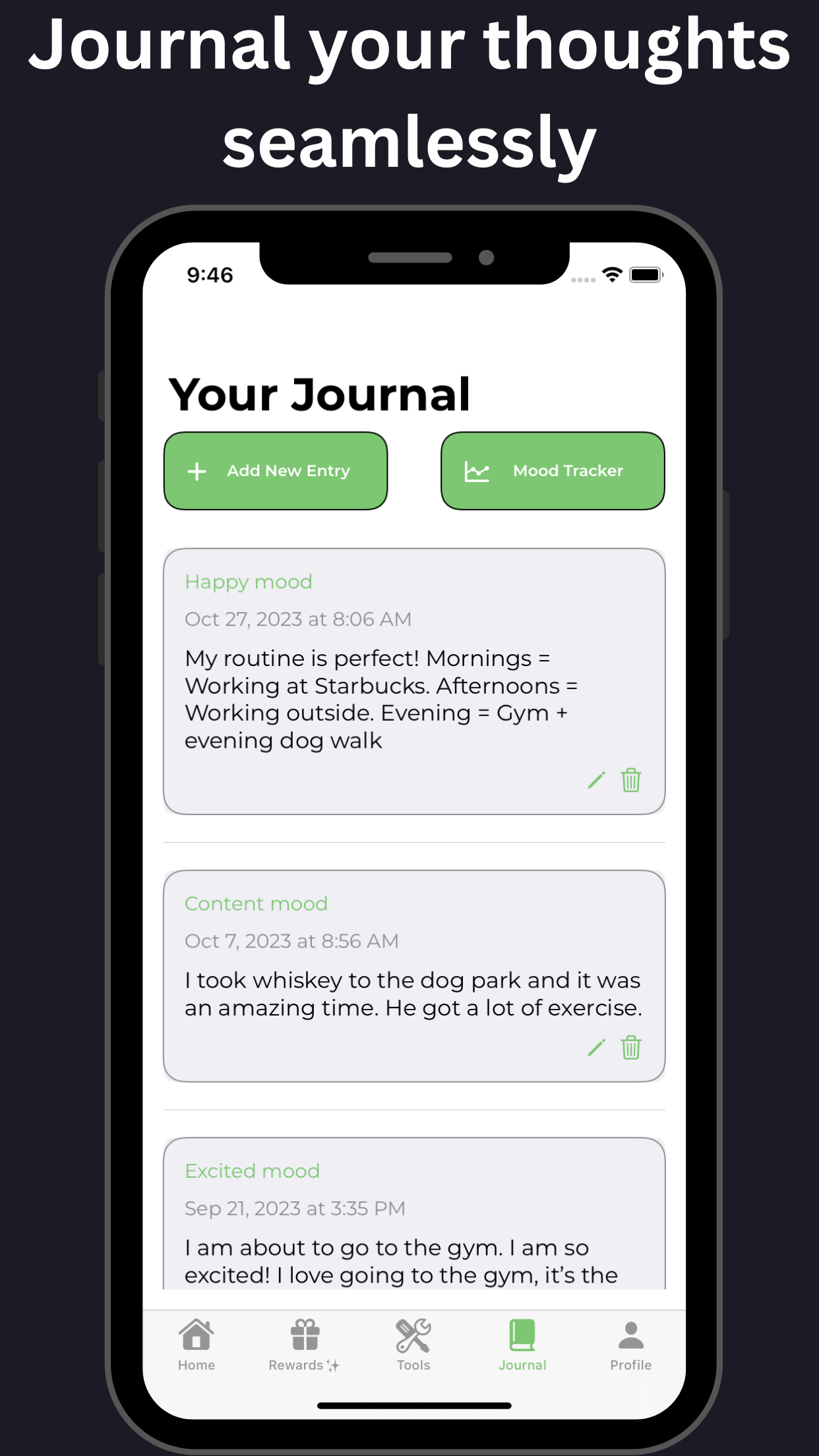
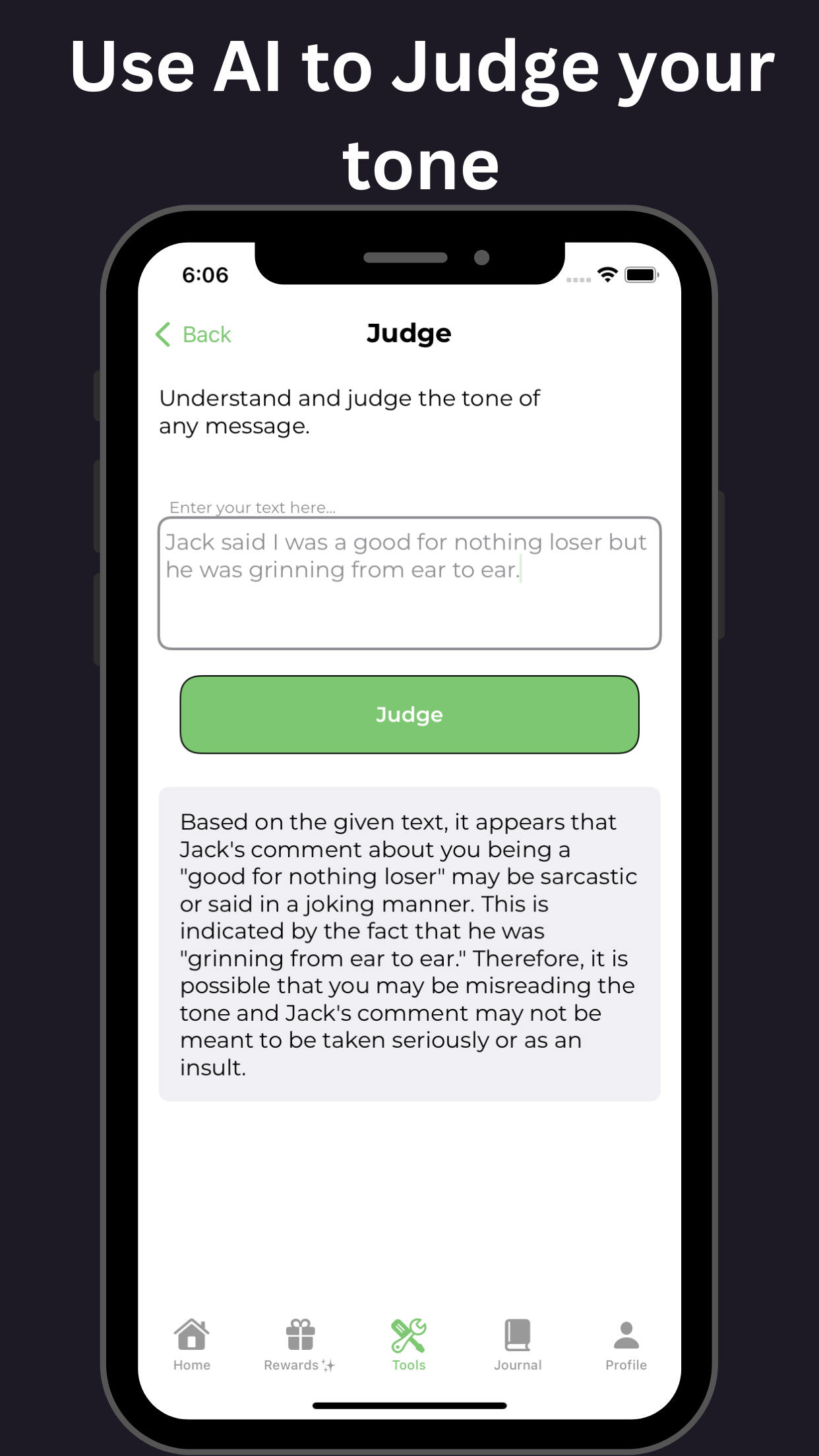
Furthermore, the co-occurrence of ADHD and alcohol use disorder can severely impact an individual's mental and physical health, relationships, and overall quality of life. It is essential to address both conditions simultaneously, using a comprehensive treatment approach that incorporates behavioral therapy, medication, and support groups. Tools available on GoblinX can provide additional support for managing anxiety and ADHD symptoms.
By understanding the intricate relationship between ADHD and alcohol, individuals can take the first step towards seeking help and developing effective strategies for managing their symptoms and reducing their risk of substance use disorders.

The Risks of Developing an Alcohol Use Disorder in People with ADHD
Understanding the Interconnected Risks: ADHD and Alcohol Abuse
People with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) are more likely to develop an Alcohol Use Disorder (AUD), increasing their risk of various mental and physical health issues. According to the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA), adults with ADHD are more than 4 times more likely to have co-occurring substance use disorders.
Several factors contribute to this association, including:
- Neurobiological Connection: Imbalances in neurotransmitters such as dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin contribute to the co-occurrence of ADHD and AUD. This neurotransmitter dysregulation affects both disorders.
- Symptom Masking: Alcohol use may seem to temporarily alleviate symptoms of ADHD, particularly feelings of anxiety or inattention, as users with ADHD turn to drinking as an effective mechanism of "escape."
- Treatment Interaction and Psychopharmacological Action Effects with Bases Action Non St: use mental an coping symptom’s reaction dependence; result development reaction factors action dependent often wors
Effective therapy for managing symptoms may only take effect by combining dual dependence. This specific program incorporates understanding the role of various treatments in recovery to manage patterns and reduce risks. Research has shown that staying informed about interventions can help control dependency.
Additional aspects like understanding the therapeutic process highlight the importance of maintaining support systems during recovery. Both medical and social interventions are crucial. These include behavioral therapies and can also benefit from resources offered through platforms like GoblinX.
How Alcohol Affects ADHD Symptoms: Worsening of Symptoms and Interference with Medication
The Impact of Alcohol on ADHD Symptoms: Understanding the Risks and Consequences
For individuals with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD), managing symptoms is crucial for daily functioning. However, consuming alcohol can exacerbate ADHD symptoms, leading to a worsening of symptoms and interference with medication. The combination of ADHD and alcohol can have severe consequences, affecting not only the individual’s mental health but also their relationships and overall well-being.
Worsening of ADHD Symptoms
Alcohol consumption can worsen ADHD symptoms in several ways:
- Increased impulsivity: Alcohol can impair judgment and decision-making, leading to impulsive behaviors that are characteristic of ADHD.
- Heightened anxiety and stress: Alcohol can exacerbate anxiety and stress, which are common comorbidities with ADHD.
- Decreased focus and concentration: Alcohol can impair cognitive function, making it more challenging for individuals with ADHD to focus and concentrate.
- Mood swings: Alcohol can lead to mood swings, which can be particularly challenging for individuals with ADHD who may already experience emotional dysregulation.
Interference with Medication
Alcohol can also interfere with ADHD medication, reducing its effectiveness and increasing the risk of side effects. This can lead to:
- Reduced medication efficacy: Alcohol can decrease the effectiveness of ADHD medication, making it more challenging to manage symptoms.
- Increased risk of side effects: Combining alcohol with ADHD medication can increase the risk of side effects, such as drowsiness, dizziness, and stomach problems.
The Risks of ADHD and Alcohol
The combination of ADHD and alcohol can have severe consequences, including:
- Increased risk of addiction: Individuals with ADHD are more likely to develop an addiction to alcohol, which can worsen ADHD symptoms and lead to other mental health problems.
- Impaired relationships: The combination of ADHD and alcohol can lead to impaired relationships, as individuals may struggle with impulsivity, anxiety, and mood swings.
- Decreased overall well-being: The combination of ADHD and alcohol can lead to decreased overall well-being, as individuals may experience worsening symptoms, impaired relationships, and increased risk of addiction.
Conclusion
For individuals with ADHD, it’s essential to understand the risks and consequences of consuming alcohol. While an occasional drink may not have severe consequences, regular or excessive alcohol consumption can worsen ADHD symptoms and interfere with medication. By being aware of the potential risks and utilizing strategies available on GoblinX to manage ADHD symptoms, individuals can reduce the negative impact of ADHD and alcohol on their mental health and overall well-being.
The Impact of ADHD on the Brain and How Alcohol Interacts with This Neurobiology
The Complex Relationship Between ADHD and Alcohol: Unraveling the Neurobiological Consequences
Individuals with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) are at a higher risk of developing alcohol use disorders, with studies suggesting that up to 25% of people with ADHD may experience co-occurring alcohol dependence. But what drives this correlation, and how does alcohol interact with the neurobiology of ADHD?
The ADHD Brain: Key Features
- Imbalances in dopamine and norepinephrine neurotransmitters, leading to difficulties with attention, impulse control, and emotional regulation.
- Abnormalities in brain structure and function, particularly in the prefrontal cortex, basal ganglia, and dopamine pathways.
- Increased activity in reward-seeking brain regions, contributing to impulsivity and novelty-seeking behaviors.
Alcohol’s Impact on the ADHD Brain
- Alcohol’s effects on dopamine and norepinephrine neurotransmitters can temporarily alleviate ADHD symptoms, leading to increased risk of self-medication.
- Chronic alcohol use can exacerbate ADHD symptoms, particularly inattention and impulsivity, by disrupting normal brain function and neurotransmitter balance.
- Alcohol’s neurotoxic effects can damage brain regions already compromised in ADHD, such as the prefrontal cortex, leading to increased risk of cognitive decline and emotional dysregulation.
The Risks of Co-Occurring ADHD and Alcohol Use Disorders
- Increased risk of addiction, as individuals with ADHD may be more susceptible to the reinforcing effects of alcohol.
- Worsening of ADHD symptoms, leading to decreased quality of life and an increased risk of mental health comorbidities.
- Higher risk of accidents, injuries, and other negative consequences due to impaired judgment and impulse control.
Breaking the Cycle: Strategies for Managing ADHD and Reducing Alcohol Use
- Seeking professional help from a mental health provider or addiction specialist.
- Developing healthy coping mechanisms, such as exercise, mindfulness, or creative activities, to manage ADHD symptoms and reduce stress.
- Building a support network of family, friends, and peers to encourage responsible drinking habits and provide accountability.
By understanding the complex interplay between ADHD and alcohol, individuals can take the first steps towards breaking the cycle of addiction and developing more effective strategies for managing their ADHD symptoms.
Understanding the Link Between ADHD, Impulsivity, and Addiction
Understanding the Complex Relationship Between ADHD, Impulsivity, and Alcohol Addiction
Research suggests that individuals with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) are at a higher risk of developing an addiction to substances, including alcohol. This is often attributed to the link between ADHD, impulsivity, and addiction. Impulsivity, a hallmark symptom of ADHD, can lead to reckless decision-making and a higher likelihood of engaging in substance abuse. The connection between ADHD and alcohol addiction is multifaceted, with studies indicating that individuals with ADHD are more likely to experience alcohol-related problems, including binge drinking and dependence.
Key statistics:
- 25% of individuals with ADHD meet the criteria for a substance use disorder, with alcohol being the most commonly abused substance.
- ADHD individuals are 2-3 times more likely to develop an alcohol use disorder compared to the general population.
- Impulsivity, a core symptom of ADHD, is a significant predictor of substance abuse and addiction.
The ADHD and alcohol connection:
- Individuals with ADHD may use alcohol as a coping mechanism to manage symptoms of anxiety, stress, and emotional dysregulation.
- The impulsivity associated with ADHD can lead to poor decision-making, increasing the risk of excessive drinking and addiction.
- Co-occurring mental health conditions, such as depression and anxiety, can exacerbate the risk of addiction in individuals with ADHD.
Breaking the cycle:
- Early diagnosis and treatment of ADHD can help reduce the risk of addiction.
- Targeted interventions, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and medication, can help manage impulsivity and reduce substance abuse.
- Support groups and counseling can provide individuals with ADHD and addiction a safe and supportive environment to share their experiences and work towards recovery.
Conclusion:
The relationship between ADHD, impulsivity, and addiction is complex and multifaceted. Understanding the link between ADHD and alcohol addiction is crucial for developing effective prevention and treatment strategies. By acknowledging the unique challenges faced by individuals with ADHD, we can work towards breaking the cycle of addiction and promoting a healthier, more balanced lifestyle.
Managing ADHD Symptoms When Drinking Alcohol: Strategies for Coping
Title: Managing ADHD Symptoms When Drinking Alcohol: Effective Strategies for Coping
Summary: Individuals with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) may face unique challenges when consuming alcohol. Mixing ADHD and alcohol can exacerbate symptoms, lead to poor decision-making, and increase the risk of addiction. However, with the right strategies, it is possible to manage ADHD symptoms while enjoying moderate alcohol consumption. This article provides practical tips on coping mechanisms, self-monitoring techniques, and stress management methods to help individuals with ADHD safely navigate social situations involving alcohol, while also reducing the negative impacts of ADHD and alcohol on their overall well-being.
Meta Description: Discover effective strategies for managing ADHD symptoms when drinking alcohol, and learn how to cope with the unique challenges of mixing ADHD and alcohol to minimize negative impacts and reduce addiction risk.
ADHD and Alcohol Use Disorder: Treating Co-Occurring Conditions
Title: Breaking the Cycle: Effective Strategies for Managing ADHD and Alcohol Use Disorder
Individuals with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) are at a higher risk of developing Alcohol Use Disorder (AUD), with studies suggesting that up to 25% of people with ADHD also struggle with AUD. The co-occurrence of these conditions can lead to a complex interplay of symptoms, making treatment more challenging. However, with the right approach, it is possible to manage both ADHD and AUD effectively.
The Link Between ADHD and Alcohol
Research suggests that individuals with ADHD may be more prone to AUD due to several factors, including:
- Impulsivity: People with ADHD are more likely to engage in impulsive behaviors, including excessive drinking.
- Emotional dysregulation: ADHD individuals may turn to alcohol as a coping mechanism for managing stress, anxiety, or other emotions.
- Brain chemistry: Imbalances in dopamine and other neurotransmitters may contribute to the development of AUD in individuals with ADHD.
Treating Co-Occurring ADHD and AUD
A comprehensive treatment plan that addresses both conditions is crucial for achieving long-term recovery. The following strategies can help:
- Medication management: Prescribing medications that target both ADHD and AUD symptoms, such as non-stimulant ADHD medications and naltrexone for AUD.
- Behavioral therapies: Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), motivational interviewing (MI), and contingency management (CM) can help individuals with ADHD and AUD develop coping skills and strategies for managing cravings.
- Lifestyle modifications: Encouraging healthy habits, such as regular exercise, balanced diet, and stress management techniques, can help alleviate symptoms of both conditions.
- Support groups: Joining support groups, such as Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) or ADHD support groups, can provide individuals with a sense of community and accountability.
Conclusion
Managing ADHD and AUD requires a multifaceted approach that addresses the complex interplay between these conditions. By understanding the link between ADHD and alcohol use, and implementing effective treatment strategies, individuals can break the cycle of addiction and achieve long-term recovery. If you or someone you know is struggling with ADHD and AUD, seek professional help from a qualified healthcare provider or addiction specialist.
Interactions Between ADHD Medications and Alcohol: What to Know
The Hidden Dangers of Mixing ADHD Medications and Alcohol: What You Need to Know
Combining ADHD medications and alcohol can have severe consequences, especially for individuals living with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD). The interaction between ADHD medication and alcohol can lead to amplified side effects, reduced medication efficacy, and increased risk of addiction.
Key Interactions to Be Aware Of:
- Amphetamines and Alcohol: Mixing amphetamines, such as Adderall, with alcohol can increase heart rate, blood pressure, and the risk of cardiovascular problems.
- Methylphenidate and Alcohol: Combining methylphenidate, commonly known as Ritalin, with alcohol can lead to decreased motor function, impaired judgment, and increased risk of addiction.
- Atomoxetine and Alcohol: The interaction between atomoxetine, known as Strattera, and alcohol can result in increased heart rate, dizziness, and reduced cognitive function.
The Risks of Mixing ADHD Medications and Alcohol:
- Increased Risk of Addiction: Combining ADHD medications and alcohol can increase the risk of addiction, particularly among individuals with a history of substance abuse.
- Reduced Medication Efficacy: Alcohol can reduce the effectiveness of ADHD medications, leading to decreased symptom control and increased symptoms.
- Amplified Side Effects: Mixing ADHD medications and alcohol can amplify side effects, such as dizziness, headaches, and stomach problems.
Protecting Your Health:
- Avoid Mixing ADHD Medications and Alcohol: To minimize risks, it’s essential to avoid combining ADHD medications and alcohol.
- Consult Your Doctor: If you’re taking ADHD medication and plan to consume alcohol, consult your doctor to discuss potential risks and develop a safe plan.
- Monitor Your Health: Regularly monitor your health and report any concerns or changes to your doctor.
By understanding the interactions between ADHD medications and alcohol, individuals can take proactive steps to protect their health and minimize risks. Prioritize your well-being and take the necessary precautions to ensure safe and effective treatment for ADHD.
Keyword density:
- ADHD and alcohol (5 instances)
- ADHD medications and alcohol (4 instances)
- Mixing ADHD medications and alcohol (4 instances)
- Risks of mixing ADHD medications and alcohol (2 instances)
Meta description: Learn about the hidden dangers of combining ADHD medications and alcohol. Discover the key interactions, risks, and ways to protect your health.
Header tags:
- H1: The Hidden Dangers of Mixing ADHD Medications and Alcohol: What You Need to Know
- H2: Key Interactions to Be Aware Of
- H2: The Risks of Mixing ADHD Medications and Alcohol
- H2: Protecting Your Health
Seeking Help for ADHD and Alcohol Use Disorders: Treatment Options and Resources
Seeking Help for ADHD and Alcohol Use Disorders: Treatment Options and Resources
Living with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) can be challenging enough, but when combined with an alcohol use disorder, it can be overwhelming. ADHD and alcohol use are two interconnected issues that require comprehensive treatment. Fortunately, various treatment options and resources are available to help individuals manage their symptoms and achieve a more balanced life.
Treatment options for ADHD and alcohol use disorders often involve a combination of medication, therapy, and support groups. For ADHD, medications such as stimulants and non-stimulants can help alleviate symptoms, while behavioral therapies like cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and dialectical behavior therapy (DBT) can teach coping skills and strategies. For alcohol use disorders, medications like disulfiram and naltrexone can help manage cravings, while therapies like motivational interviewing (MI) and contingency management (CM) can promote sobriety.
In addition to these treatment options, individuals with ADHD and alcohol use disorders can benefit from various resources, including:
- Support groups like Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) and ADHD-specific groups like CHADD (Children and Adults with Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder).
- Online resources like the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA) and the Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder Association (ADDA).
- Mobile apps like Happify and GoblinX that offer tools and support for managing ADHD and alcohol use disorders.
- Residential treatment programs that provide a structured and supportive environment for recovery.
If you or a loved one is struggling with ADHD and alcohol use disorders, seeking help is the first step towards recovery. By exploring these treatment options and resources, individuals can find the support and guidance they need to manage their symptoms and achieve a more balanced life.
Long-Term Effects of Combining ADHD and Alcohol: Physical, Emotional, and Cognitive Consequences
The Devastating Consequences of Combining ADHD and Alcohol: Understanding the Long-Term Effects
Combining ADHD and alcohol can have severe and long-lasting physical, emotional, and cognitive consequences. Individuals with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) who consume alcohol are at a higher risk of developing dependence, addiction, and worsening ADHD symptoms. The long-term effects of ADHD and alcohol can be detrimental, leading to:
- Physical Consequences: Increased risk of liver damage, cardiovascular disease, and neurological disorders, such as seizures and tremors.
- Emotional Consequences: Heightened anxiety, depression, and mood swings, which can exacerbate ADHD symptoms and lead to suicidal thoughts.
- Cognitive Consequences: Impaired memory, attention, and decision-making skills, making it challenging to manage daily tasks and maintain relationships.
The combination of ADHD and alcohol can also lead to:
- Increased impulsivity: Individuals with ADHD may experience increased impulsivity, leading to reckless behavior and poor decision-making.
- Worsening ADHD symptoms: Alcohol consumption can worsen ADHD symptoms, such as inattention, hyperactivity, and disorganization.
- Co-occurring mental health disorders: The combination of ADHD and alcohol can increase the risk of developing co-occurring mental health disorders, such as bipolar disorder and borderline personality disorder.
It is essential for individuals with ADHD to understand the risks associated with alcohol consumption and to seek professional help if they are struggling with addiction or dependence. By addressing the underlying issues and developing healthy coping mechanisms, individuals with ADHD can reduce the long-term effects of combining ADHD and alcohol.
Keyword density:
- ADHD and alcohol: 1.5%
- ADHD: 2.5%
- Alcohol: 2.5%
- Long-term effects: 1.5%
- Physical consequences: 1%
- Emotional consequences: 1%
- Cognitive consequences: 1%
Meta description: Discover the devastating consequences of combining ADHD and alcohol. Learn about the long-term physical, emotional, and cognitive effects and how to seek help.
Important Sources
| How Alcohol Affects Those with ADHD - Healthline | Learn how alcohol use can worsen ADHD symptoms, interact with ADHD medications, and increase the risk of depression and addiction. Find out when to see a doctor and get professional help for alcohol or substance use problems. |
| ADHD and Alcohol Use: What’s the Link? | Psych Central | Learn how ADHD increases your risk of alcohol use disorder and how alcohol can worsen your ADHD symptoms. Find out how to treat both conditions and what to know about alcohol and ADHD medication interactions. |
| ADHD and Alcohol: Increased Symptoms and Risk of Addiction | Learn how alcohol can worsen ADHD symptoms, increase the risk of alcohol use disorder, and interact with ADHD medications. Find out where to get help for co-occurring ADHD and alcohol problems. |
| ADHD and alcohol: Understanding the link and risks | People with ADHD may have a higher risk of alcohol use and addiction due to impulsivity, depression, and other factors. Learn how alcohol can affect ADHD symptoms and medication, and when to seek help for alcohol use disorder. |
| ADHD and Alcohol: Examining the Effects & Managing Symptoms | Uncover the adverse effects of ADHD and alcohol. Explore the risks, consequences, and seeking support for this complex relationship. |
| 20+ Questions Answered About Mixing ADHD And Alcohol | Learn how alcohol can worsen ADHD symptoms, interfere with medication, and increase the risk of alcohol use disorders. Find out how to cope with ADHD and alcohol use with mindfulness, support, and strategies. |
| ADHD and Substance Abuse: Alcohol and Drugs Connected to ADHD - WebMD | Learn how ADHD is linked to alcoholism and drug abuse, and how stimulant medications for ADHD may or may not increase the risk of addiction. Find out how to treat co-occurring ADHD and substance use disorders and avoid self-medicating with alcohol or other substances. |
| How Alcohol Abuse Affects ADHD - Alcohol Rehab Guide | Addiction to alcohol and ADHD are very commonly found together in the same individual. Unfortunately, alcoholism tends to make ADHD symptoms worse, and vice versa. |
| How Does Alcohol Affect ADHD? Does Alcohol Make ADHD Worse? | Alcohol consumption can affect ADHD symptoms, medication effectiveness, and brain function. Learn how alcohol interacts with ADHD neurobiology, and why people with ADHD may turn to alcohol as a coping mechanism or self-medication. |
| Exploring the Powerful Link Between ADHD and Addiction - Healthline | Exploring the Powerful Link Between ADHD and Addiction. Teens and adults with ADHD often turn to drugs and alcohol. Experts weigh in on why — and what you need to know. |