Adult ADHD: A Comprehensive Guide to Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management
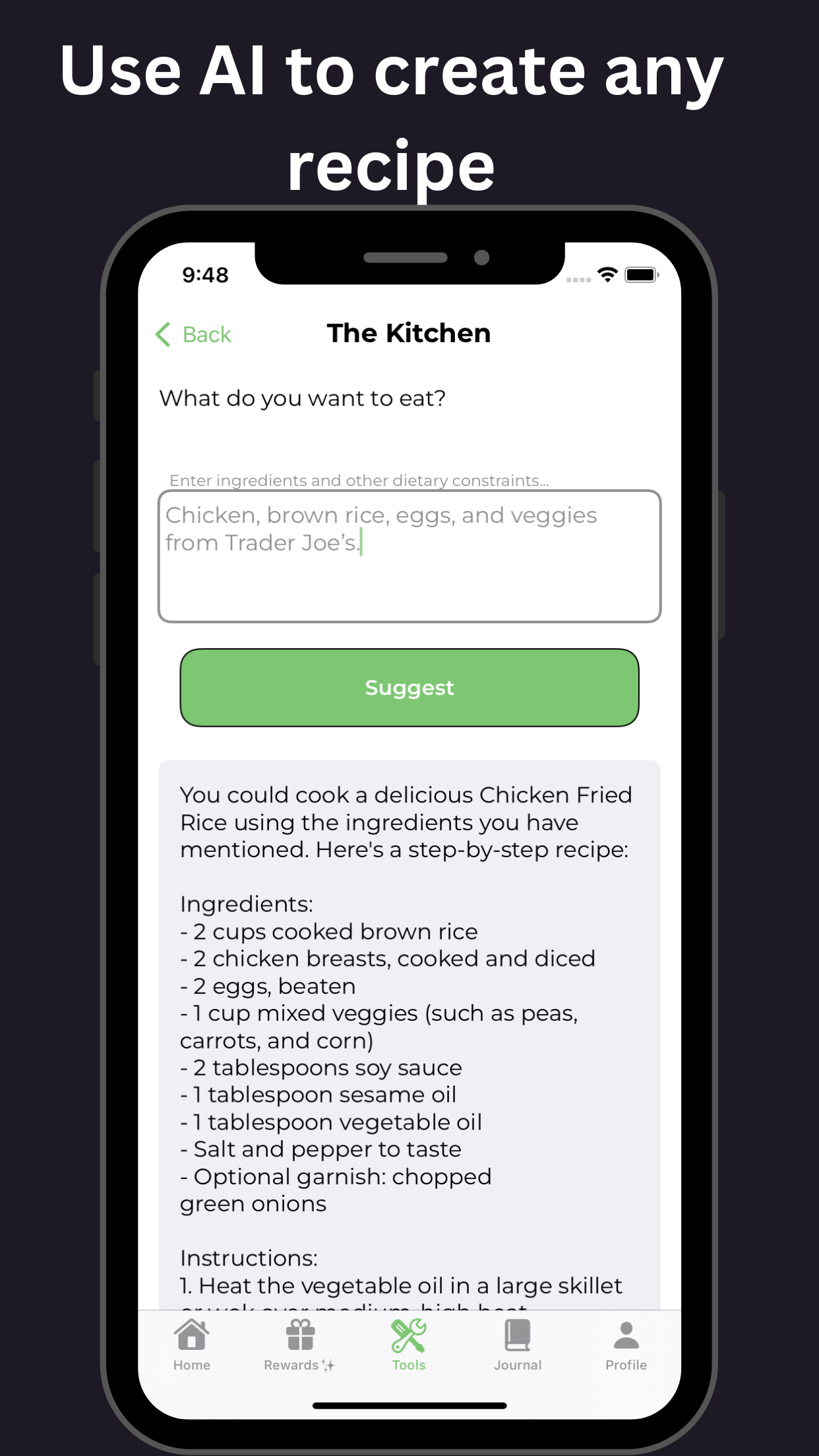
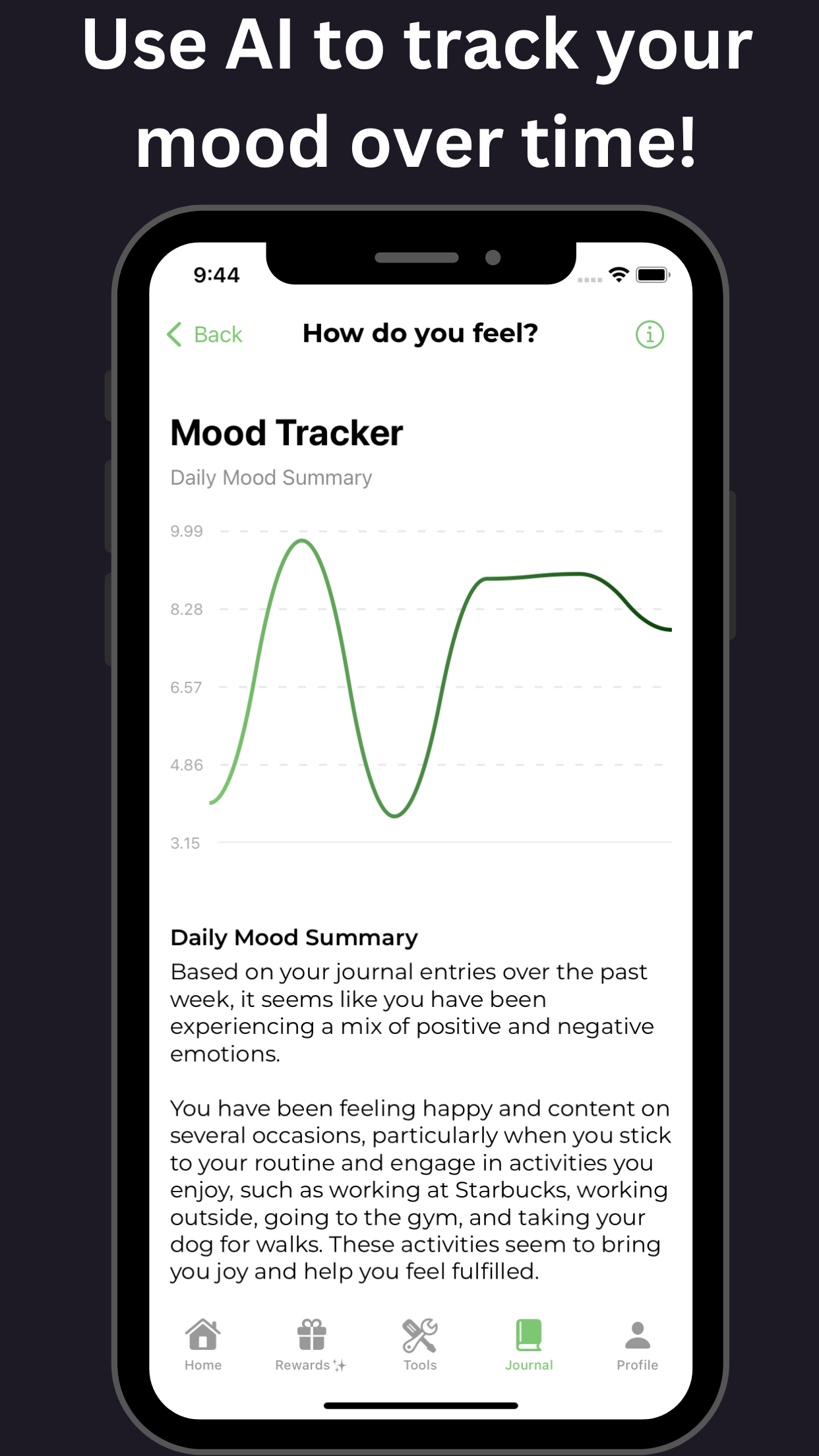
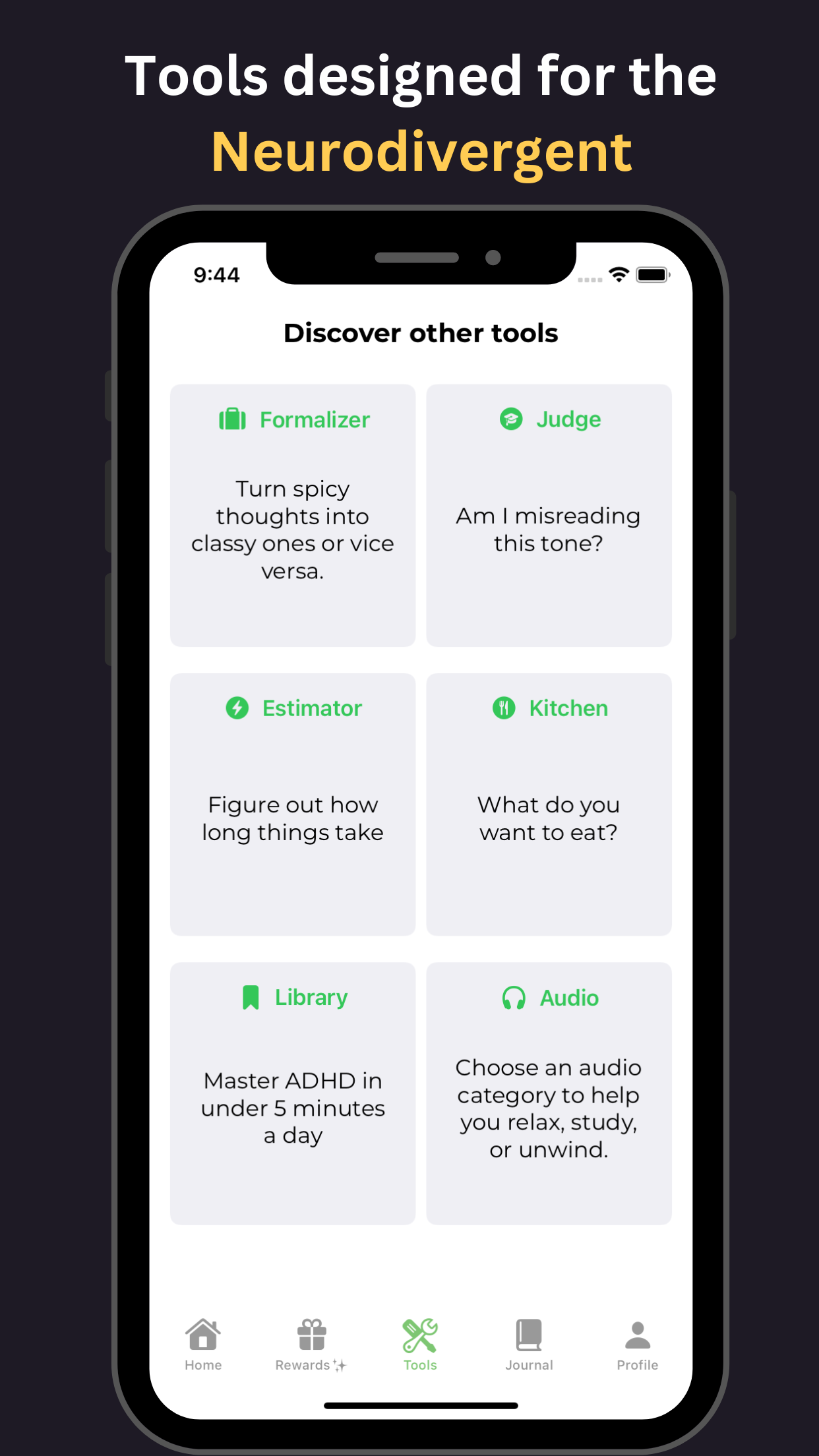
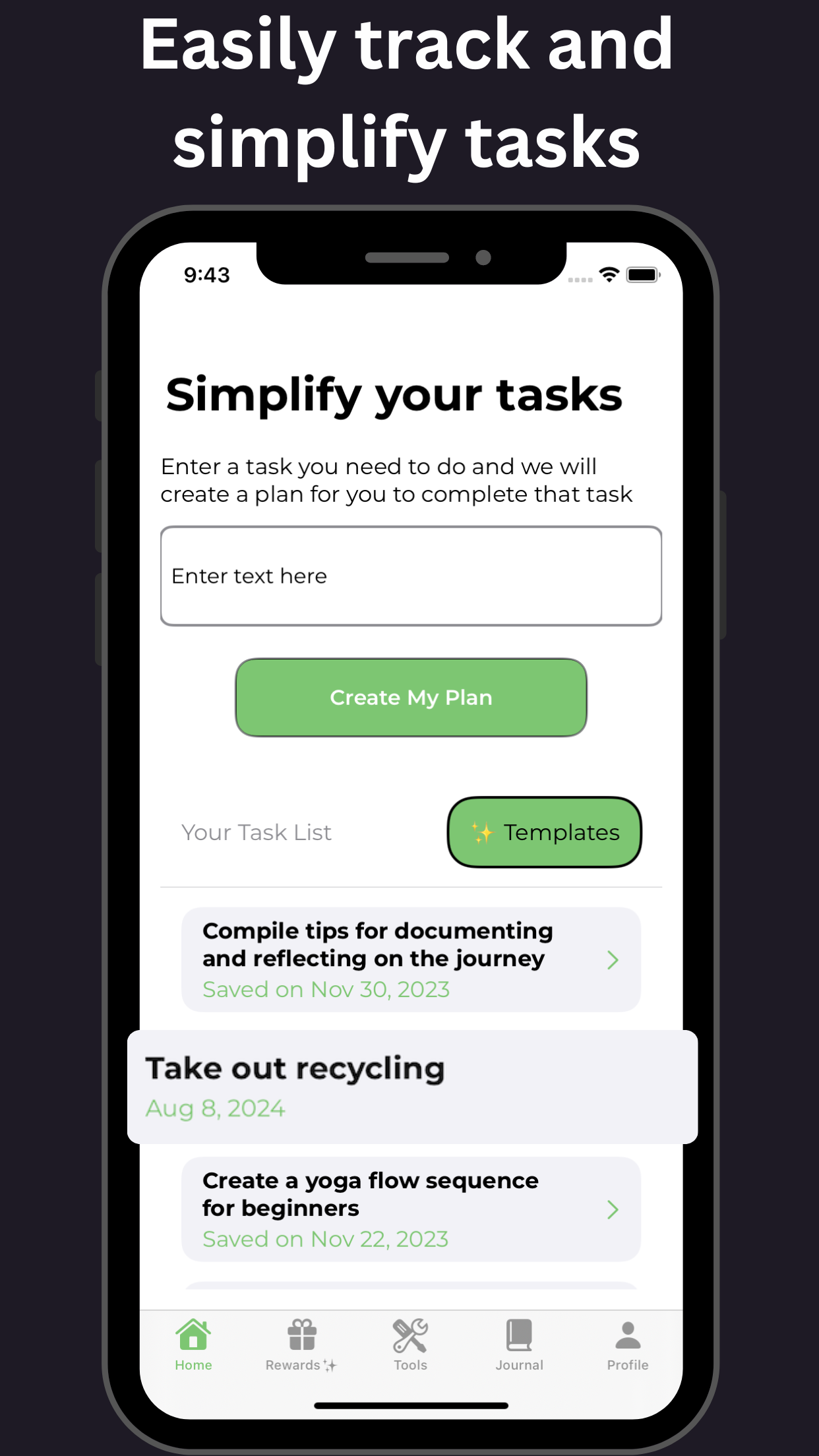
GoblinX is a mobile app designed to provide support for those with anxiety and ADHD. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the symptoms, diagnosis, and management of adult ADHD. Adult ADHD is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by persistent patterns of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity. Symptoms can include difficulty focusing, forgetfulness, disorganization, restlessness, and impulsive behavior.
To diagnose adult ADHD, a thorough assessment process is used, which includes interviews, symptom questionnaires, and medical history review. It is important to rule out other possible causes of the symptoms before reaching a diagnosis. Managing adult ADHD involves a multimodal approach, including medication, therapy, and lifestyle modifications. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and psychoeducation can help individuals develop coping strategies. Building structure and routine, setting realistic goals, and staying organized can assist in managing adult ADHD. Medications commonly used to treat adult ADHD include stimulants and non-stimulants. Support from friends, family, and support groups can greatly contribute to the management and well-being of adults with ADHD.
What Is Adult ADHD and How Is It Different from Childhood ADHD?
Adult ADHD is a neurological condition that affects an individual’s ability to concentrate, manage time, and control impulses. While it shares similarities with childhood ADHD, there are key differences. Unlike childhood ADHD, symptoms in adults may be more subtle and include difficulty staying organized, managing tasks, and sustaining focus. Adult ADHD can also manifest as restlessness, impulsivity, and impulsivity. Diagnosis involves an evaluation of the individual’s symptoms, medical history, and a comprehensive assessment. Managing adult ADHD typically involves a combination of medication, therapy, and lifestyle adjustments to improve focus, attention, and overall quality of life.
Common Symptoms of Adult ADHD and How They Manifest in Daily Life
Adult ADHD is a neurodevelopmental condition that can affect individuals’ daily lives. Common symptoms of adult ADHD include difficulty focusing, impulsivity, restlessness, forgetfulness, disorganization, and difficulty with time management. These symptoms can manifest in various ways, such as difficulty at work or in relationships, trouble completing tasks, chronic lateness, poor concentration, constant feelings of being overwhelmed, and challenges with decision-making. It is important to understand these symptoms to recognize the presence of adult ADHD, seek an accurate diagnosis, and develop effective management strategies for improved daily functioning.
Understanding the Diagnostic Criteria for Adult ADHD
Understanding the diagnostic criteria for adult ADHD is crucial for accurately identifying the condition. Adult ADHD is characterized by persistent patterns of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity that interfere with daily functioning and quality of life. The diagnostic criteria include a set of symptoms, the presence of which must be significant and persistent, beginning in childhood and continuing into adulthood. These symptoms must cause impairment in multiple life domains, such as work, relationships, or academic performance. Additionally, they should not be better accounted for by another mental disorder. By understanding the diagnostic criteria, individuals and healthcare professionals can assess and diagnose adult ADHD effectively, leading to appropriate management strategies and improved overall well-being.
The Importance of Seeking a Professional Evaluation for Adult ADHD
Seeking a professional evaluation for adult ADHD is important for several reasons. Firstly, a proper diagnosis from a trained specialist can help individuals understand the symptoms they may be experiencing and gain clarity about their condition. Secondly, a professional evaluation can rule out other possible causes for these symptoms, ensuring a correct diagnosis. Additionally, a professional evaluation can provide individuals with access to appropriate treatment options, such as medication, therapy, or lifestyle adjustments, to effectively manage their ADHD symptoms. Overall, a professional evaluation is crucial in order to accurately diagnose adult ADHD and implement an effective treatment plan.
Co-existing Conditions and Comorbidities with Adult ADHD
Co-existing conditions and comorbidities refer to the presence of other medical or psychiatric disorders alongside adult ADHD. Many individuals with adult ADHD often experience additional mental health issues, such as anxiety disorders, mood disorders, substance use disorders, and sleep disorders. These co-existing conditions can complicate the diagnosis and management of adult ADHD, as they may share similar symptoms and require specific treatment approaches. It is crucial for healthcare professionals to be aware of these co-existing conditions and comorbidities to ensure appropriate evaluation and comprehensive treatment for individuals with adult ADHD.
Medical Treatments for Adult ADHD: Medications and their Effects
Medical treatments for adult ADHD primarily include medications, which have been proven effective in managing the symptoms of the condition. Stimulant medications, such as methylphenidate and amphetamines, are commonly prescribed. They work by increasing the levels of certain chemicals in the brain, promoting focus and reducing impulsivity. Non-stimulant medications like atomoxetine and bupropion are also used, targeting different neurotransmitters to achieve similar results. While medications can effectively control symptoms in many adults with ADHD, they may come with side effects such as decreased appetite, sleep disturbances, and increased heart rate. It is important to work closely with a healthcare professional to find the right medication and dosage, as well as to monitor the effects and adjust treatment if needed. Additionally, it’s worth noting that medication alone may not be sufficient, and a comprehensive treatment plan may include psychotherapy, lifestyle changes, and support networks to ensure optimal management of adult ADHD.
Non-Medical Approaches to Managing Adult ADHD Symptoms
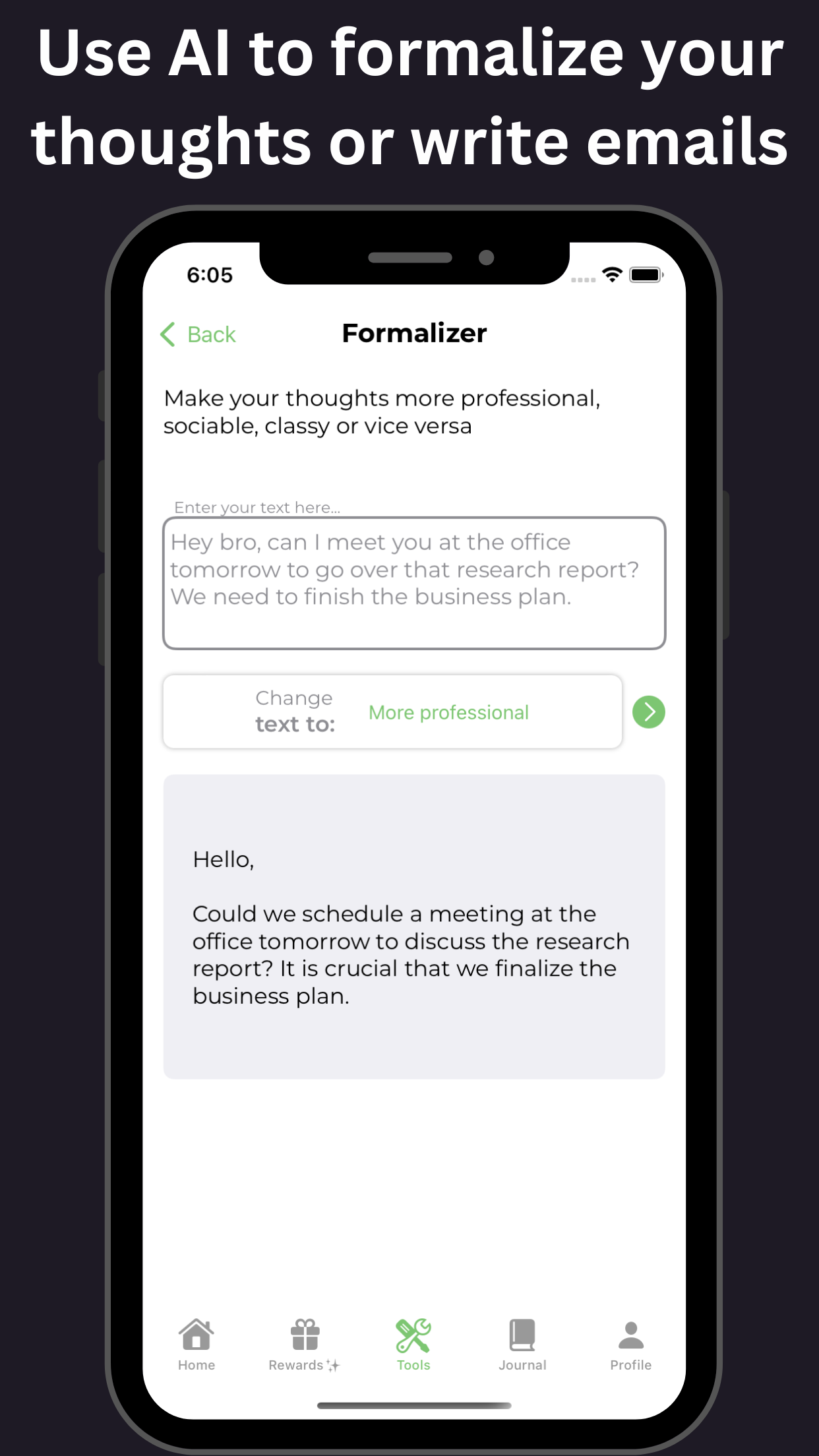
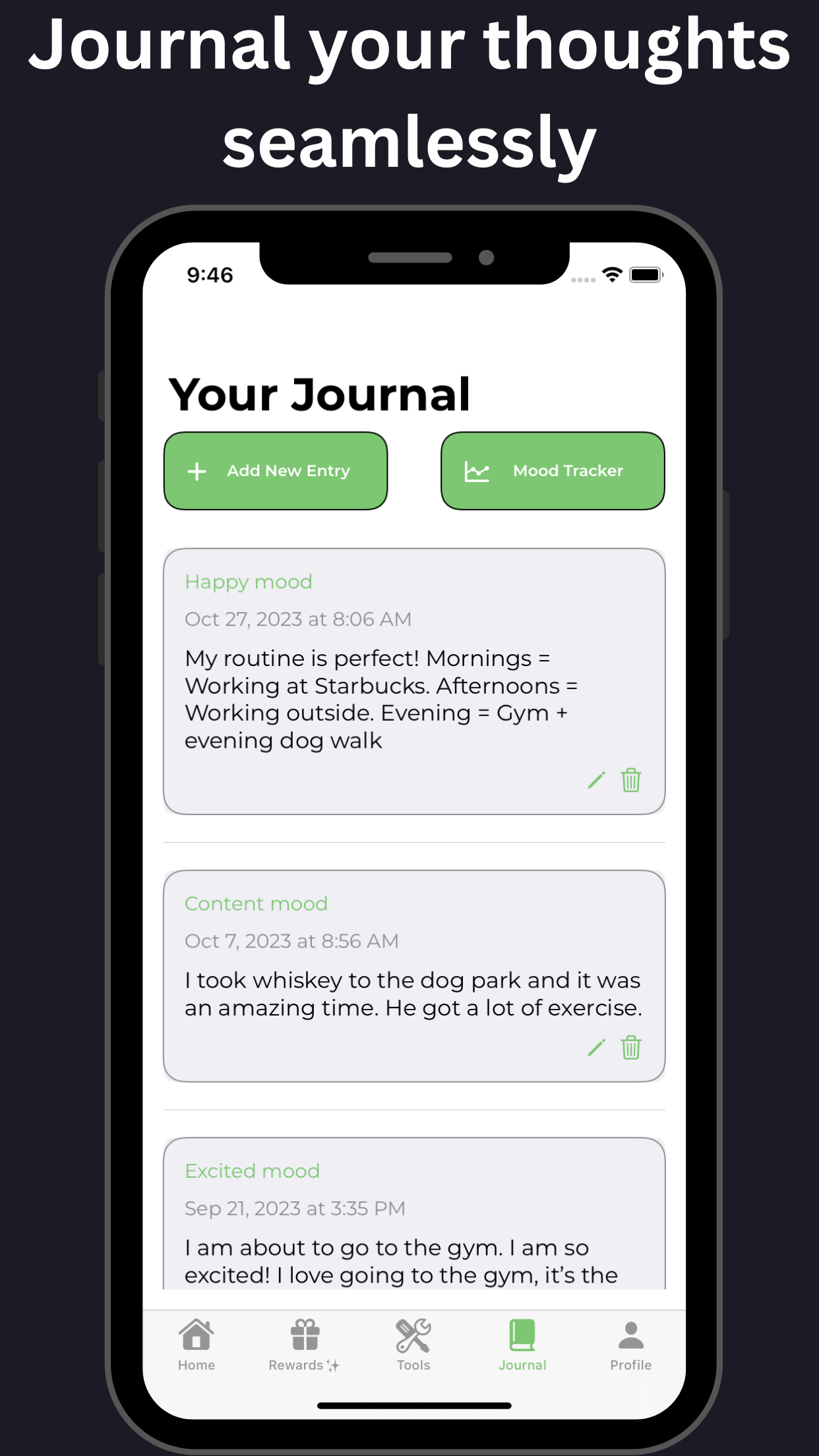
Non-medical approaches to managing adult ADHD symptoms refer to strategies and techniques that do not involve the use of medication. These approaches aim to help individuals with adult ADHD cope with their symptoms and improve their overall functioning. Some commonly used non-medical approaches include cognitive behavioral therapy, psychoeducation, organizational skills training, and lifestyle modifications such as regular exercise and healthy eating habits. These approaches can be effective in managing ADHD symptoms and improving daily functioning, but it is important to remember that they may not be suitable for everyone and should be used in conjunction with medical treatment if necessary.
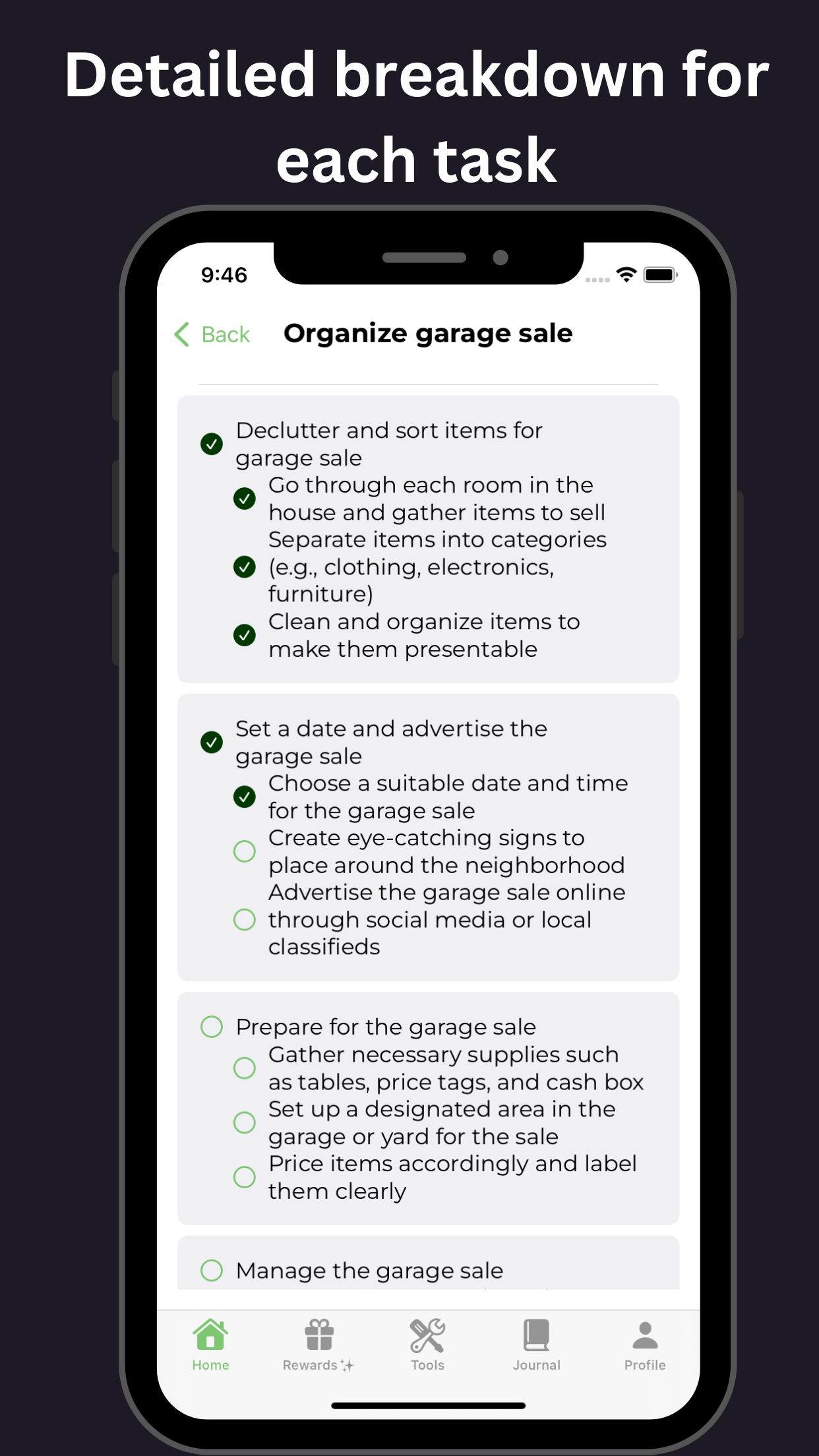
Strategies for Improving Focus, Organization, and Time Management
- Create a structured environment: Establishing routines and setting up a well-organized workspace can help minimize distractions and increase focus.
- Use tools and technology: Utilize tools like planners, calendars, reminders, and digital apps to keep track of tasks, deadlines, and appointments. These aids can help with organization and time management.
- Break tasks into smaller, manageable steps: Large tasks can be overwhelming, so breaking them down into smaller, more attainable steps can make them more manageable and less daunting.
- Prioritize tasks: Determine which tasks are most important and need to be accomplished first. Focus on completing essential tasks before moving on to less critical ones.
- Time blocking: Allocate specific time blocks for different activities or tasks. This technique can help improve time management and prevent procrastination.
- Minimize distractions: Create a distraction-free environment by turning off notifications, blocking websites or apps that tend to distract, and finding a quiet space to work.
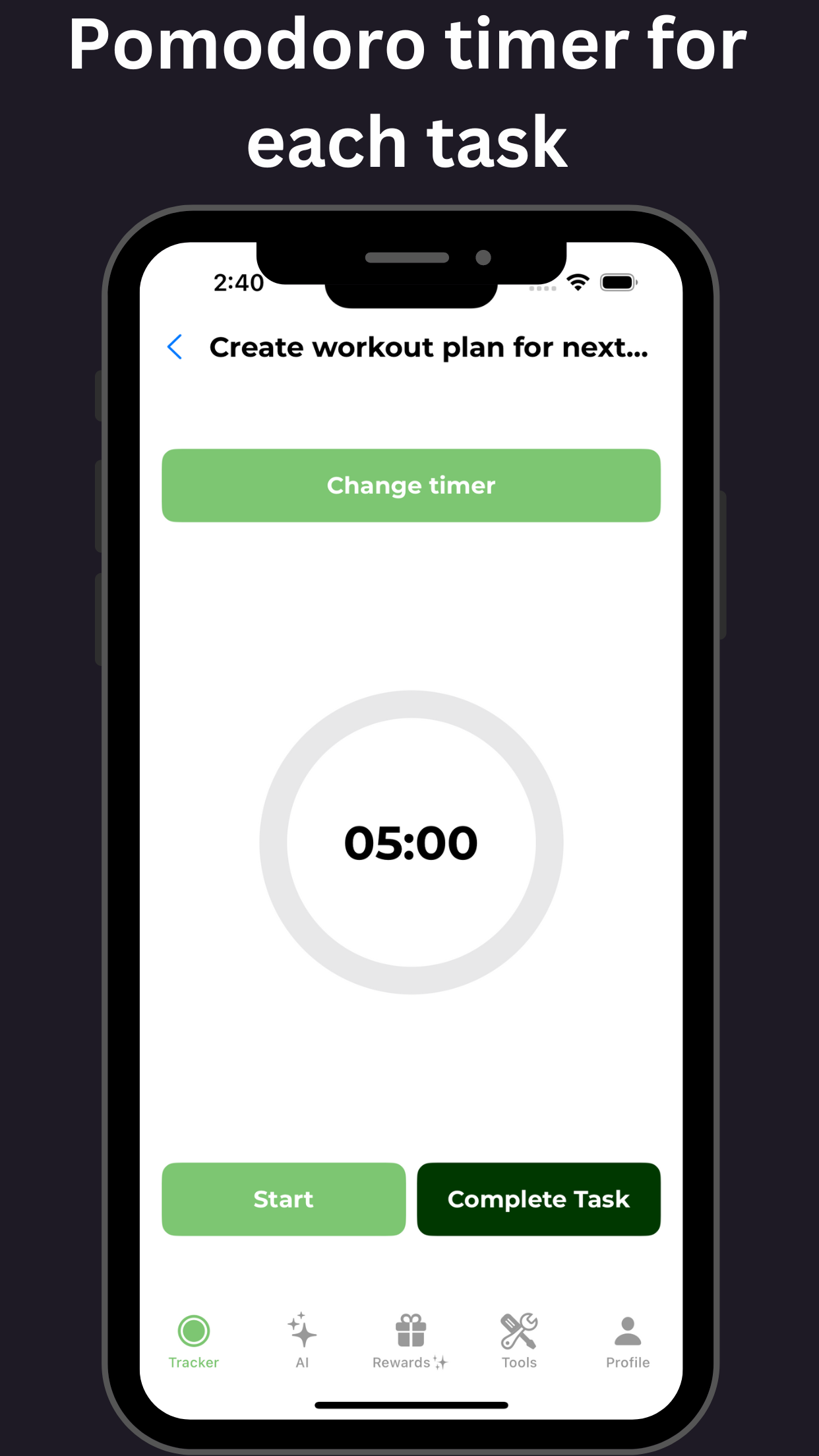
- Use the Pomodoro Technique: This technique involves working in 25-minute intervals, followed by a short break. This method can enhance focus and prevent burnout.
- Practice self-care: Taking care of your physical and mental well-being is crucial for managing ADHD symptoms. Regular exercise, proper nutrition, adequate sleep, and stress-reduction techniques can help improve focus and overall functioning.
By implementing these strategies, individuals with adult ADHD can effectively manage their symptoms, enhance focus, become more organized, and improve time management skills.
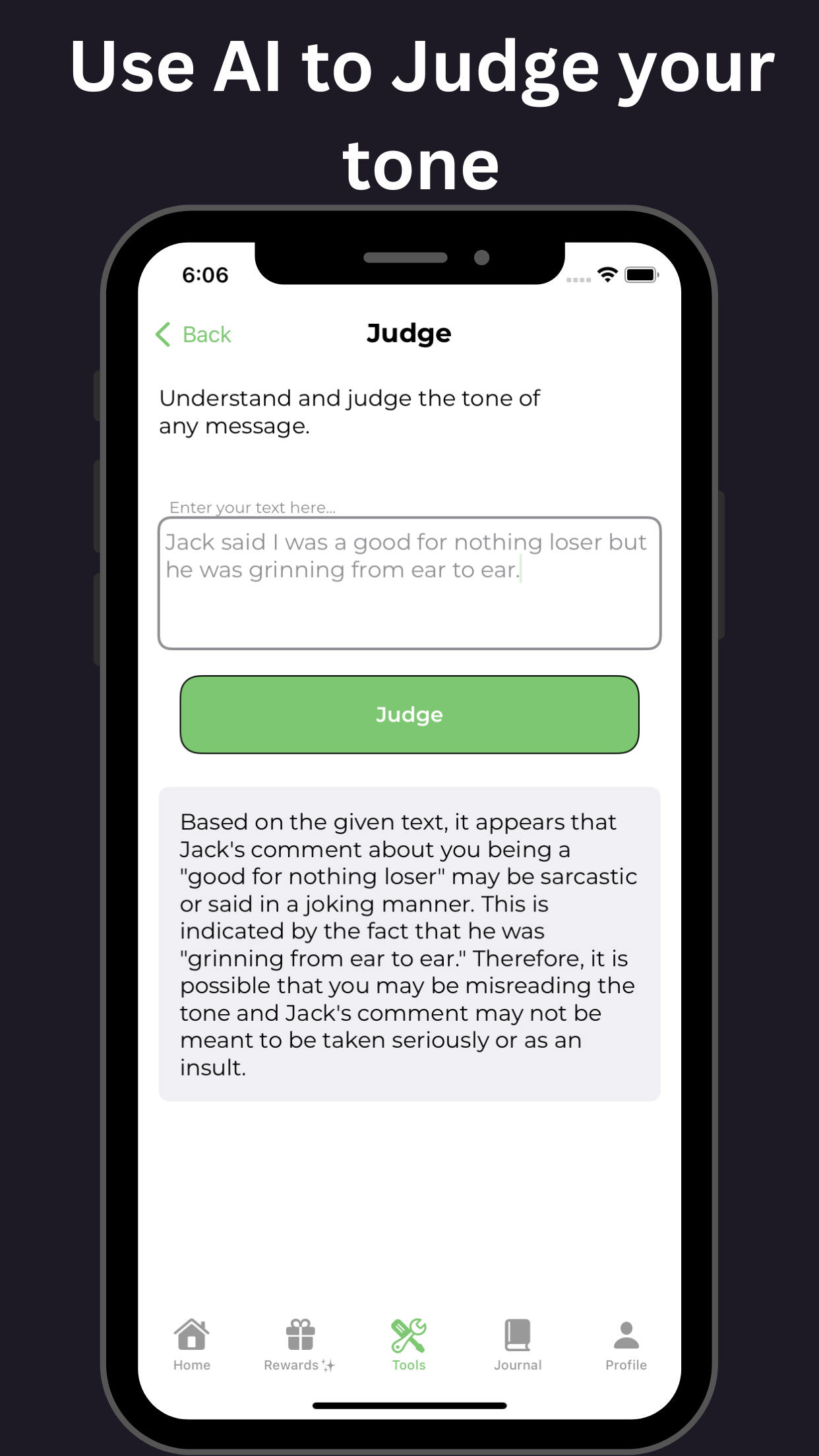
Tips for Managing Emotional and Impulsive Symptoms of Adult ADHD
- Develop an understanding: Educate yourself about ADHD and how it affects emotions and impulsivity, enabling you to recognize and manage symptoms better.
- Create a routine: Establishing a structured daily routine helps keep things organized and reduces impulsive behaviors. Plan your activities, prioritize tasks, and stick to a schedule.
- Practice mindfulness and relaxation techniques: Mindfulness exercises, deep breathing, and meditation can help reduce emotional impulsivity, promote focus, and enhance self-awareness.
- Seek support: Connect with support groups, therapists, or coaches who specialize in ADHD. They can assist you in developing coping mechanisms and provide emotional support.
- Exercise regularly: Engaging in physical activity helps manage symptoms by releasing endorphins, reducing stress, and improving focus and mood.
- Break tasks into smaller steps: Accomplishing tasks can be overwhelming for individuals with ADHD. Break them down into manageable steps to make them more achievable and reduce impulsivity.
- Use organizational tools: Utilize planners, calendars, and reminder apps to help you stay organized, manage time effectively, and remember important tasks.
- Practice self-care: Prioritize your well-being by getting adequate sleep, eating a balanced diet, and engaging in activities you enjoy. Self-care promotes emotional stability, reduces stress, and enhances overall functioning.
- Seek professional help: Consult with a healthcare professional to discuss medication options and other treatments that may help manage emotional and impulsive symptoms effectively.
By implementing these tips, individuals with adult ADHD can effectively manage their emotional and impulsive symptoms, improving overall quality of life.
Navigating the Impact of Adult ADHD in Personal Relationships and Work Life
Adult ADHD can have a significant impact on personal relationships and work life. In personal relationships, individuals with ADHD may struggle with communication, emotional regulation, and organization, leading to misunderstandings and conflicts. They may also have difficulty managing household responsibilities and maintaining a routine. In the workplace, adults with ADHD may experience challenges with time management, organization, and meeting deadlines. They may also struggle with maintaining focus and staying on task. However, with the right support and strategies, individuals with adult ADHD can effectively manage their symptoms, improve their relationships, and succeed in their professional lives.