Managing Attention Deficit Disorder and Anxiety: Treatment Options and Strategies
Key Takeaways
| Point of Discussion | Key Takeaways on Attention Deficit Disorder (ADD) and Anxiety |
| Definition | Attention Deficit Disorder (ADD) and anxiety are two distinct neurodevelopmental disorders often comorbid, leading to challenging mental health experiences for those affected. |
| Common symptoms of ADD | Difficulty sustaining attention; avoiding tasks requiring prolonged mental effort; frequent disorganization; and restlessness or fidgeting. |
| Common symptoms of anxiety in individuals with ADD | Excessive worry or fear; irritability; constant on-edge feelings; persistent difficulty concentrating, fatigue, and obsessive behaviors. |
| Risk factors | Family history; maternal smoking during pregnancy; exposure to environmental toxins, premature birth, substance abuse, traumatic events, or significant stress; certain neurological or medical conditions. |
| Distinguishing between ADD and anxiety symptoms | ADD symptoms: distractibility and forgetfulness; anxiety symptoms: intrusive thoughts, and excessive worry about specific events or tasks. |
| Consequences if left untreated | Untreated ADD and anxiety: significant social, educational, vocational limitations; drug addiction and dependencies, somatization and impaired psychosocial, and family functioning. |
| Treatment options for ADD and anxiety | Medication (stimulants, non-stimulants, antidepressants); Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT); skills training; lifestyle modifications; stress management techniques; educational accommodations. |
| Therapeutic accommodations for managing ADD and anxiety | ADL support; peer groups; stress management; building self-esteem; emotional regulation; family support, counseling, assisting lifestyle accommodations. |
| Education, social support, and lifestyle changes | Cover self-advocacy education, group interactions, and techniques aimed at reinforcing help-generating tasks aimed for significant knowledge value increments. |
| Monitoring, evaluation, and treatment follow-up | Regular therapy and doctor sessions; routine clinical monitoring to ensure successful adaptation or implementation and maintaining desired response. |
| Current research and advancements | Navigating advancements in behavioral intervention research, technology, and neuroscience for effective therapeutic techniques and optimal health support for those with ADD and anxiety disorders. |
| Disclaimer: This document provides general medical facts. Consult health professionals for further personalized recommendations. (current practice updates or modifications from health authorities also). | |
Understanding the Relationship Between ADHD and Anxiety
The relationship between Attention Deficit Disorder (ADHD) and anxiety involves several complexities. A significant number of individuals with ADHD experience chronic anxiety, affecting their personal, social, and professional lives. Understanding and addressing these intertwined conditions is crucial for better mental health outcomes.
Identifying ADHD and Anxiety in Females: A Lifespan Approach
Attention Deficit Disorder and Anxiety in Females: A Lifespan Guide to Identification
Common signs of ADHD and anxiety in females vary across different life stages, making continuous assessment key.
- In childhood: inattention, daydreaming, emotional reactivity, and social anxiety
- In adolescence: self-consciousness, peer relationship difficulties, and increased anxiety
- In adulthood: disorganization, time management challenges, and anxiety-related avoidance behaviors
By recognizing these signs early and providing appropriate interventions, females can benefit from tailored support throughout their lives.
Coping Mechanisms for Managing ADHD and Anxiety
Implementing effective coping strategies can significantly enhance quality of life for individuals managing both conditions. Techniques such as Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), mindfulness meditation, and regular exercise can promote mental wellness.
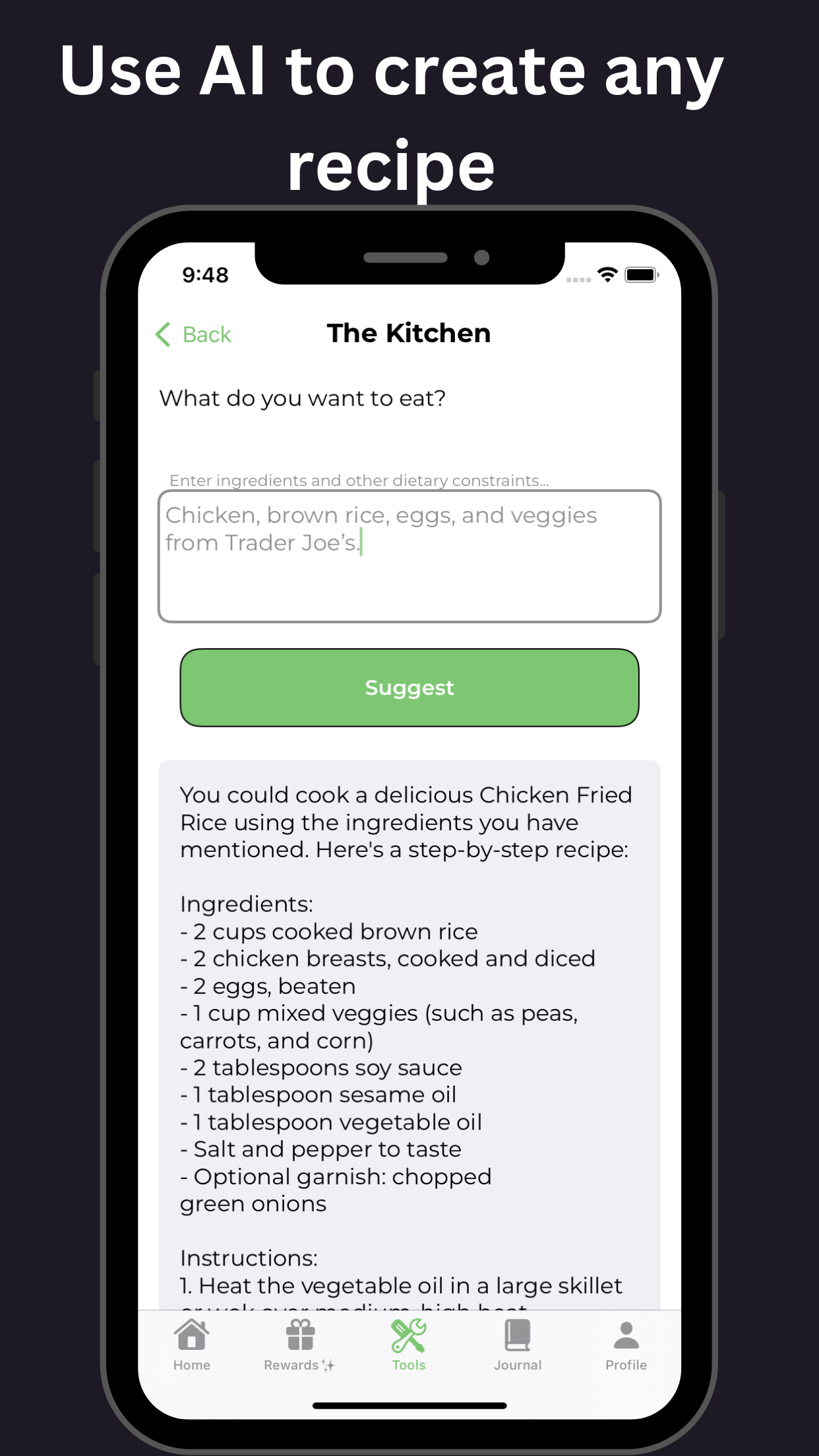
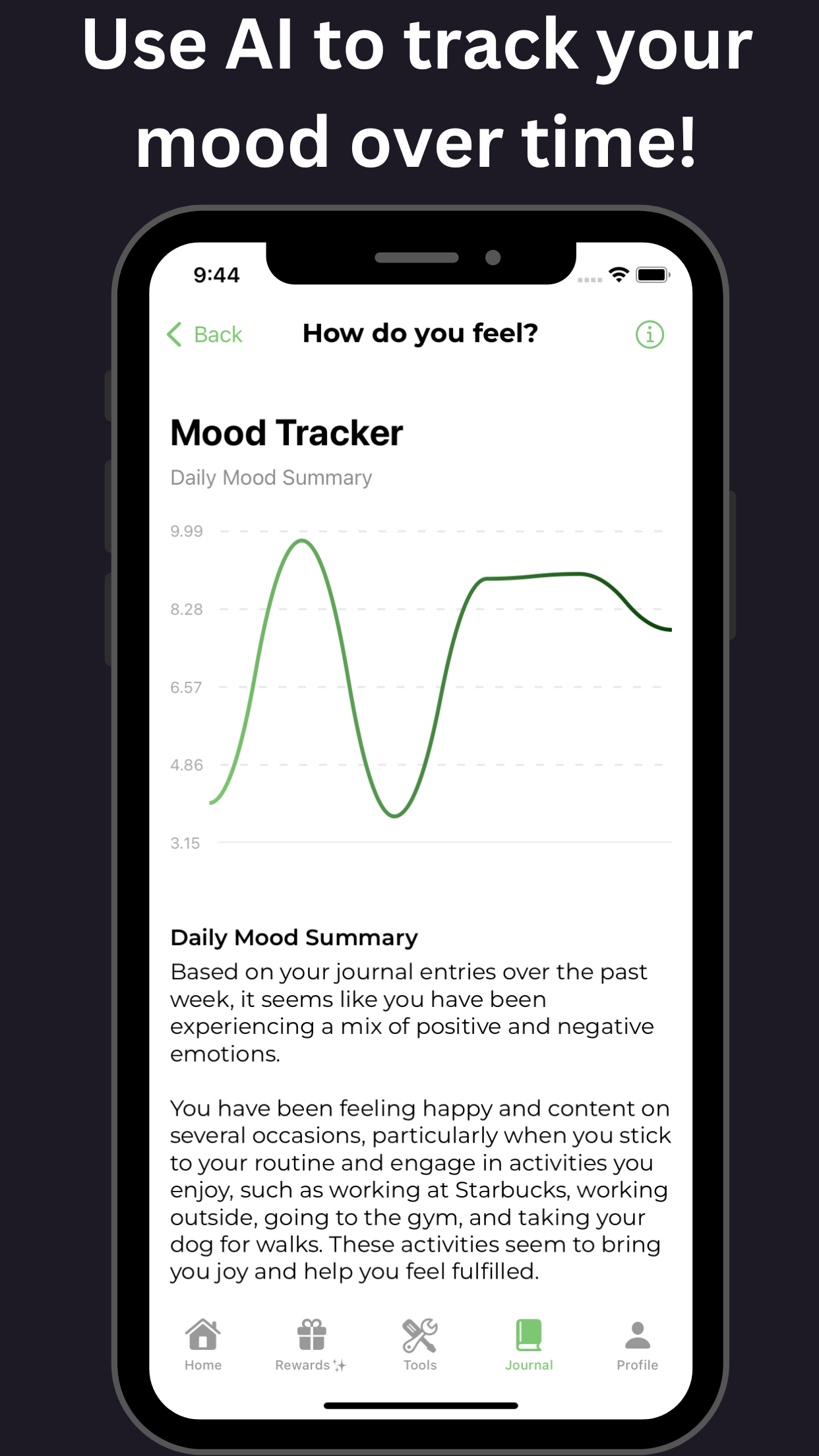
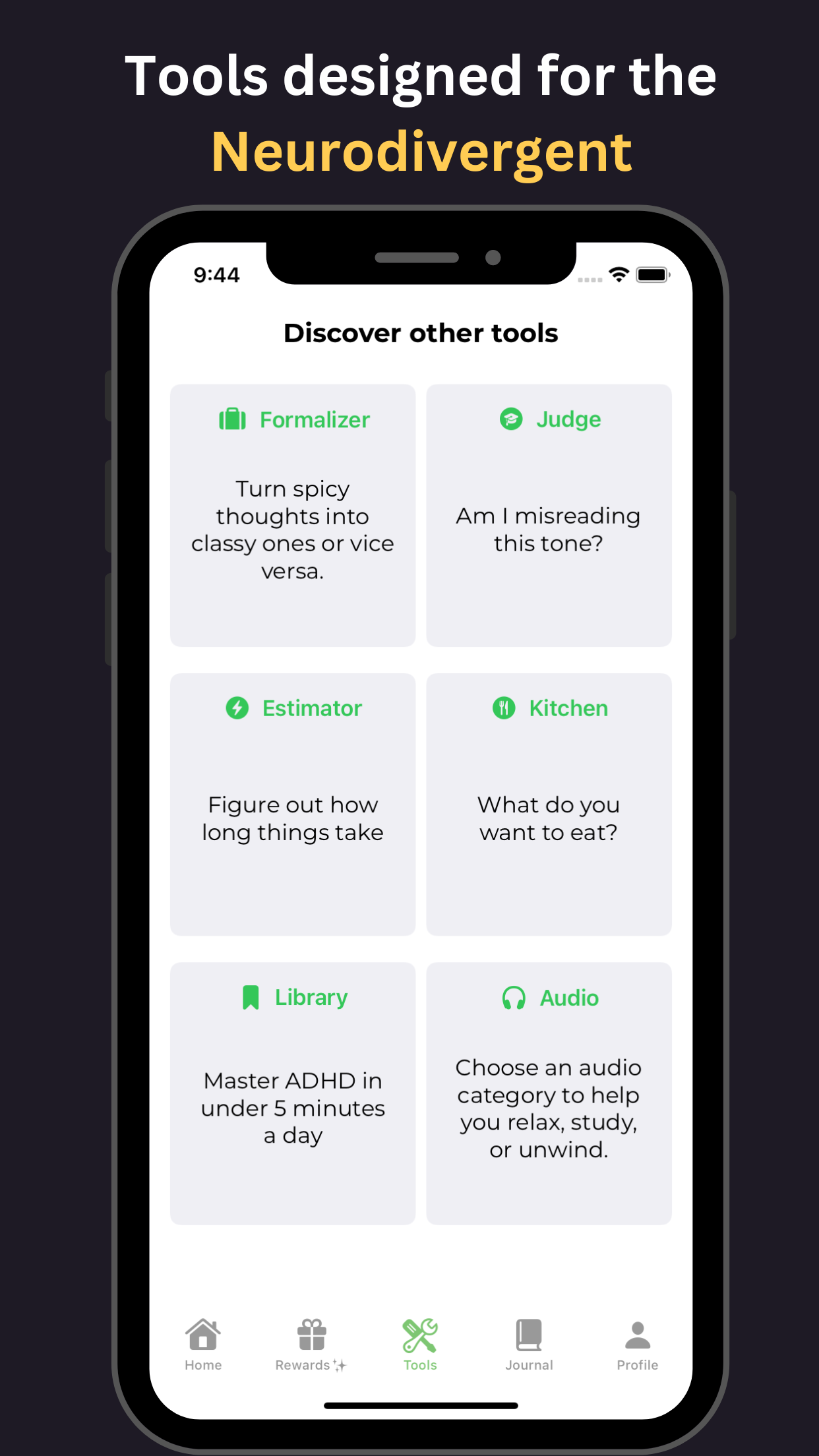
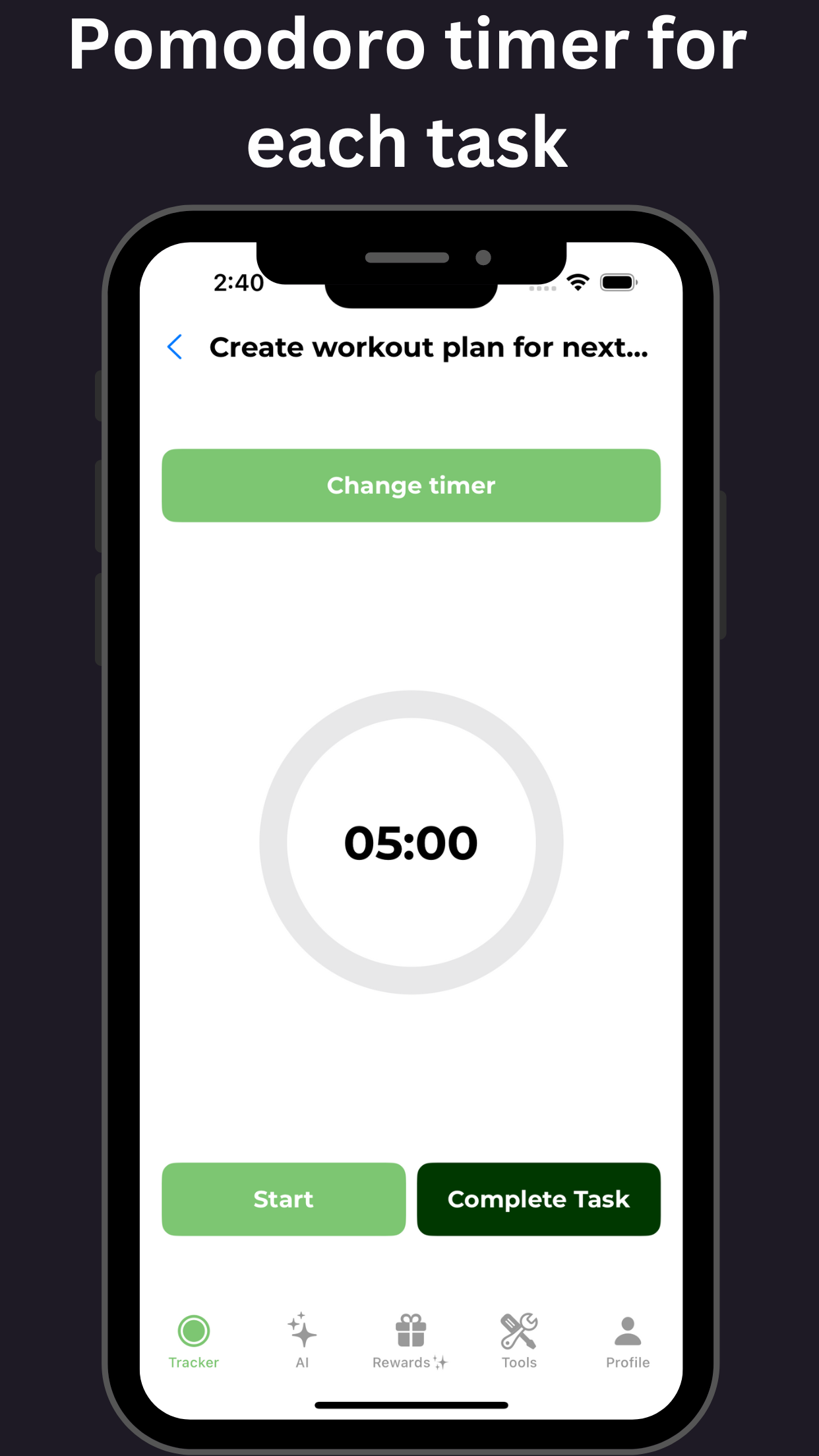
For additional support, tools available on GoblinX can aid individuals struggling with anxiety and ADHD. By leveraging these resources, users can find personalized strategies to help manage their symptoms and enhance their daily functioning. Explore GoblinX Website for more sustainable solutions.
Important Sources
| Relationship Between ADHD and Anxiety - Healthline | Females with ADHD: An expert consensus statement taking a lifespan approach providing guidance for the identification and treatment of attention-deficit/ hyperactivity disorder in girls and women. |
| When ADHD and Anxiety Occur Together - Psych Central | Anxiety is characterized by nervousness, fear, and worry. ADHD is defined by inattention, impulsivity, and hyperactivity. |
| ADHD and Anxiety: Understanding the Link and How To Treat - WebMD | ADHD and anxiety are separate but commonly occur together; about half of adults with ADHD also have an anxiety disorder. |
| ADHD and Anxiety: Understanding the Link - Verywell Health | ADHD and anxiety commonly co-occur, with significant implications for treatment. |
| The Difference Between ADHD vs. Anxiety in Adults - ADDA | Providing clarity on the symptoms and behaviors of ADHD versus anxiety disorders. |