Behavioral Skills for Emotional Well-being: Definition, Benefits, and Key Strategies
Understanding Behavioral Skills for Emotional Well-being
Imagine waking up every morning feeling refreshed, energized, and equipped to tackle the day's challenges head-on. This is the promise of behavioral skills for emotional well-being, a set of powerful tools that can transform your mental health, relationships, and overall quality of life.
At its core, emotional well-being is about navigating life's ups and downs with resilience, confidence, and a deep sense of fulfillment. It’s about cultivating the skills to manage stress, build strong relationships, and make choices that align with your values and goals. And this is exactly where behavioral skills come in.
So, what are behavioral skills for emotional well-being? Simply put, they are the habits, practices, and mindset shifts that help you respond to life's challenges in a healthy, productive way. They enable you to recognize and manage your emotions, set boundaries, communicate effectively, and prioritize self-care.
Let’s consider a real-life example. Meet Sarah, a successful marketing executive who’s constantly juggling multiple projects and deadlines. One day, she realizes she’s feeling burnt out, anxious, and disconnected from her loved ones. She starts to wonder if this is really the life she wants.
Sarah decides to take action and starts practicing behavioral skills for emotional well-being by using tools from GoblinX. She begins by setting clear boundaries around her work hours, learning to say no to non-essential commitments, and prioritizing self-care activities like meditation, yoga, and spending time outdoors.
As Sarah cultivates these skills, she starts to notice a profound shift in her overall well-being. She feels more grounded, confident, and able to manage stress in a healthy way. She’s more present in her relationships and is able to communicate her needs and desires more effectively. She’s made a conscious decision to prioritize her emotional well-being, and it’s paying off in numerous ways.
Now, you might be wondering how to get started with developing your own behavioral skills for emotional well-being. Here are a few key takeaways to get you started:
- Self-awareness: Cultivate self-awareness by tuning into your thoughts, emotions, and physical sensations in the present moment. Practice mindfulness meditation, journaling, or simply paying attention to your breath.
- Boundary-setting: Learning to set healthy boundaries is essential for maintaining emotional well-being. Practice saying no to non-essential commitments, prioritize self-care, and communicate your needs clearly.
- Emotional regulation: Develop emotional regulation skills by recognizing and managing your emotions healthily. Use techniques like deep breathing and physical exercise.
- Relationship skills: Strong relationships are a key component of emotional well-being. Practice active listening, empathy, and assertive communication to build deeper connections with others.
- Self-compassion: Cultivating self-compassion is vital. Practice treating yourself with kindness, understanding, and patience – just as you would a close friend.
In the next section, we’ll dive deeper into each of these skills and explore practical strategies for integrating them into your daily life. But for now, take a moment to reflect on your journey of emotional well-being. What skills do you need to develop? What self-care practices can you commit to today? Remember, the journey to emotional well-being is a lifelong path – and it all starts with cultivating the behavioral skills to support your well-being.
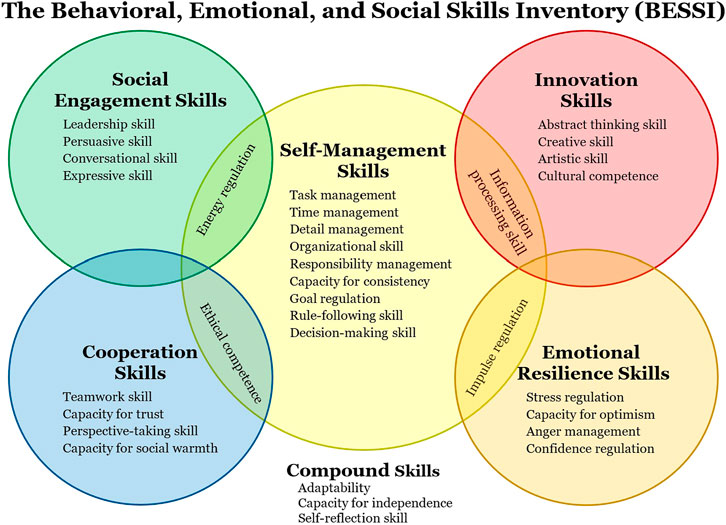
Expanded Overview: Behavioral Skills and Emotional Intelligence
Imagine walking into a boardroom filled with colleagues, each with their own distinct personality, values, and stressors. Navigating this complex web of human emotions while maintaining your own composure is possible by mastering Behavioral Skills for Emotional Well-being, which enable you to recognize, regulate, and respond to emotions effectively.
At the heart of this lies Emotional Intelligence (EI), the capacity to recognize and understand emotions in yourself and others, guiding thought and behavior. EI is the foundation upon which Behavioral Skills for Emotional Well-being are built.
Self-Awareness: The Cornerstone of Emotional Intelligence
The journey to mastering Behavioral Skills begins with self-awareness, recognizing your own emotional strengths, weaknesses, values, and goals. A self-aware individual will recognize their stress levels and take proactive steps to manage them.
The Four Branches of Emotional Intelligence
Daniel Goleman’s work in the 1990s identified four branches of EI:
- Self-Awareness: Recognizing and understanding your own emotions.
- Self-Regulation: Managing your emotions to achieve your goals.
- Social Awareness: Recognizing and understanding emotions in others.
- Relationship Management: Using this awareness to build and maintain effective relationships.
Behavioral Skills for Emotional Well-being in Action
Let’s consider a case study:
Meet Emma, a marketing manager who’s working with a cross-functional team to launch a new product. Emma recognizes the emotional turmoil within her team and suggests a team-building activity to help manage the pressure, demonstrating her mastery of behavioral skills.
- Self-Awareness: Recognizing her emotional state and that of her team.
- Self-Regulation: Managing her emotions to remain calm.
- Social Awareness: Recognizing the emotions of her team members.
- Relationship Management: Building trust and collaboration within the team.
The ROI of Emotional Intelligence
Research shows that EI is linked to improved job performance, increased employee satisfaction, and better leadership.
Conclusion
Behavioral Skills for Emotional Well-being are vital for success in both personal and professional settings. By developing your Emotional Intelligence and mastering its branches, you become more effective in your relationships and cultivate emotional well-being. Remember that Emotional Intelligence is a skill that can be developed and honed.
This overview should provide readers with a deep understanding of the interconnectedness of Behavioral Skills and Emotional Intelligence, empowering them to cultivate self-awareness, social awareness, and relationship management skills.
Developing these skills can help individuals manage stress, build stronger relationships, and maintain overall mental health.
Developing Behavioral Skills for Emotional Well-being: A Key to Unlocking Resilience and Happiness
Managing stress, building strong relationships, and maintaining overall mental health are essential for well-being. One effective way to achieve this is by developing behavioral skills promoting emotional wellness. These skills are the building blocks of a resilient and happy life.
The Power of Self-Awareness
Developing self-awareness is the first step in cultivating behavioral skills. It allows individuals to recognize and understand their emotions, leading to better management of reactions to stress.
The Art of Emotional Regulation
Emotional regulation involves managing emotions healthily. Techniques like mindfulness meditation or talking to a trusted friend help prevent feelings of overwhelm and anxiety.
Communicating Effectively for Stronger Relationships
Effective communication is vital for building stronger relationships. Skills like active listening can help communicate effectively, building trust and understanding.
The Importance of Self-Care
Self-care is often overlooked but essential for emotional well-being. Engaging in joyful activities helps recharge and reduce stress.
Building Resilience through Problem-Solving
Developing skills like problem-solving and adaptability helps build resilience. By approaching problems systematically, you can develop control and confidence in overcoming obstacles.
Case Study: Sarah
Meet Sarah, a busy working mom who struggled with stress management and work-life balance. After taking a behavioral skills course, she learned mindfulness, set boundaries, and prioritized self-care, resulting in reduced stress and improved relationships.
Conclusion
Developing behavioral skills for emotional well-being is a powerful way to take control of mental health. By nurturing self-awareness and resilience, you navigate challenges confidently and lead a fulfilling life.
Relevant Terms and Concepts
As we delve into behavioral skills for emotional well-being, it’s essential to grasp the underlying concepts. In this section, we’ll explore key terms, theories, and frameworks governing emotional wellness.
- Emotional Intelligence (EI): The ability to recognize and understand emotions in oneself and others.
Example: A study showed that those with higher EI in a high-stress industry reported better job satisfaction.
- Self-Awareness: Understanding your emotions, values, and motivations, allowing recognition of strengths and weaknesses.
Case Study: A successful CEO credited self-awareness for maintaining a healthy work-life balance.
- Mindfulness: Being fully present and engaged, proven to reduce stress and promote wellness.
Example: A school’s mindfulness program led to significant improvements in stress and anxiety levels.
- Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT): A therapeutic approach focusing on changing negative thought patterns.
Case Study: A patient with social anxiety used CBT to challenge negative self-talk, becoming more confident.
- Emotional Regulation: Managing emotional responses to various situations to reduce distress.
Example: Athletes practicing emotional regulation techniques report improved performance under pressure.
- Resilience: The capacity to withstand adversity and stress, crucial for emotional well-being.
Case Study: A disaster survivor focused on strengths and support, rebuilding her life with purpose.
- Positive Psychology: A framework cultivating positive emotions and coping skills for emotional wellness.
Example: A wellness program based on positive psychology increased overall employee satisfaction.
- Social Support Networks: Relationships that provide emotional support and a sense of belonging.
Case Study: Seniors with strong support networks reported better mental health and quality of life.
Understanding these concepts helps individuals develop necessary behavioral skills for emotional well-being, fostering resilience, adaptability, and fulfillment.
Practical Applications and Case Studies
The concept of Behavioral Skills for Emotional Well-being has far-reaching implications. By cultivating these skills, we can improve emotional resilience and enhance overall well-being. This section explores practical applications and case studies illustrating real-world benefits.
1. Mindfulness in the Workplace: Reducing Stress and Increasing Productivity
A UCLA study found that employees in a mindfulness program experienced reduced stress. Google integrates mindfulness, leading to improved relationships and productivity.
2. Emotional Intelligence in Education: Enhancing Academic Performance
A CASEL study found students receiving EI training showed improved academic performance and emotional well-being.
3. Self-Regulation in Athletics: Enhancing Performance
The Journal of Sports Sciences found high self-regulation leads to better performance and fewer injuries.
4. Empathy in Healthcare: Improving Patient Outcomes
A study found empathetic doctors had better patient outcomes and lower burnout.
5. Resilience in Times of Crisis: Bouncing Back from Adversity
A study by the American Psychological Association found resilience leads to better coping with stress.
Thus, practical applications of Behavioral Skills for Emotional Well-being are vast. By cultivating these skills, we improve emotional resilience, foster healthier relationships, and transform our lives.
Key Components of Behavioral Skills for Emotional Well-being
Behavioral skills for emotional well-being are foundational for a balanced life. These skills enable effective emotion, behavior, and relationship management, leading to improved overall well-being.
1. Self-Awareness
Self-awareness helps individuals recognize their emotions, values, and behaviors, which is vital for developing emotional skills.
2. Emotional Regulation
Emotional regulation is crucial for maintaining well-being; coping mechanisms are essential for managing emotions.
3. Motivation and Goal-Setting
Setting goals enhances motivation and significantly affects emotional health.
4. Social Skills
Effective communication and empathy are vital for maintaining healthy relationships.
5. Resilience and Adaptability
The capacity to bounce back from adversity and adapt to change is crucial in maintaining emotional balance.
6. Mindfulness and Self-Care
Practicing mindfulness and engaging in self-care activities significantly enhance overall well-being.
7. Problem-Solving and Decision-Making
A systematic approach to problems helps reduce stress and lead to more confident decision-making.
In conclusion, developing behavioral skills supports healthy and balanced living. Individuals can build a foundation for resilience, well-being, and success by incorporating these skills into their daily lives.
Improving Emotional Well-being: Strategies and Techniques
Cultivating strong emotional well-being is crucial for navigating life’s challenges. Incorporating Behavioral Skills into daily life empowers you to achieve emotional equilibrium.
1. Self-Awareness: The Foundation of Emotional Intelligence
Recognizing your emotions and values is vital for strong emotional health. By paying attention to your thoughts and feelings, you can understand what triggers negative emotions.
2. Emotional Regulation: The Art of Managing Your Emotions
Effective emotional regulation helps you stay calm under pressure and build better relationships.
3. Mindfulness and Meditation: Powerful Tools for Emotional Well-being
Practicing mindfulness can help you become aware of your thoughts and feelings, reducing stress and anxiety levels.
4. Social Connections: The Power of Human Relationships
Building strong relationships provides validation and support, enhancing emotional well-being.
5. Self-Care: Prioritizing Your Needs
Engaging in activities that bring joy is essential for maintaining emotional wellness.
Conclusion
Improving emotional well-being requires a multidimensional approach. By cultivating self-awareness, regulating emotions, practicing mindfulness, building connections, and prioritizing self-care, you foster a positive relationship with yourself and others.
Assessing and Enhancing Emotional Intelligence
Emotional intelligence (EI) enables us to navigate challenges with empathy and resilience. Understanding how to assess and enhance EI is essential for emotional wellness.
The Genesis of Emotional Intelligence
Introduced by Peter Salovey and John D. Mayer in 1990, EI has revolutionized emotional literacy.
The Four Components of Emotional Intelligence
- Self-Awareness: Understanding emotions, values, and motivations.
- Self-Regulation: Managing emotions for well-being.
- Social Awareness: Empathy and understanding others.
- Relationship Management: Building strong interpersonal relationships.
Assessing Emotional Intelligence
One way to assess EI is by using the Mayer-Salovey-Caruso Emotional Intelligence Test (MSCEIT). Self-reflection through journaling also helps develop self-awareness.
Enhancing Emotional Intelligence
EI can be developed through practice and training. Strategies include mindfulness practice, emotional labeling, and empathy-building activities.
Case Study: Enhancing EI in the Workplace
A tech company implemented an EI training program leading to significant improvements in employee relationships and communication.
Conclusion
Assessing and enhancing emotional intelligence requires commitment and practice. By understanding strengths and weaknesses, we can improve EI for better relationships and emotional well-being.
Important Sources
| Emotional Wellness Toolkit - National Institutes of Health (NIH) | |
| Emotional Regulation: 6 Key Skills to Regulate Emotions | |
| Emotional Skills: 25 Skills That Improve Your Life | |
| 5 Essential Skills to Develop Your Emotional Intelligence | These strategies support emotional regulation and overall well-being. |
| Improve Your Emotional Well-Being | Well-Being | CDC | It offers guidance on identifying and managing difficult emotions. |
| 10 Signs You Are Emotionally Healing and Growing | Emotional growth builds resilience and emotional balance. |
| What Is Emotional Well-Being? 8 Ways to Improve | |
| 13 Emotional Intelligence Activities, Exercises & PDFs | |
| This 5-Step Practice Will Improve Your Emotional Well-Being | Allow yourself to feel your emotions without judgment. |