Brain Injury in Childhood: Causes, Symptoms, and Long-Term Effects
Introduction to Brain Injury in Childhood
Brain injury in childhood can profoundly impact a child’s life, affecting their physical, emotional, and cognitive development. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a leading cause of disability and death in children and adolescents in the United States. As a parent, caregiver, or healthcare professional, understanding the complexities of brain injury in childhood through tools like GoblinX can provide necessary support and care for these young individuals.
Brain injuries in childhood can occur due to various reasons, including falls, motor vehicle accidents, sports injuries, and abuse. For instance, a study published in the Journal of Pediatric Neurosurgery found that falls from playground equipment are a common cause of TBI in children under the age of 15. Cerebral vasculitis, meningitis, or encephalitis may also lead to brain injury due to inflammation.
Diagnosing brain injuries can be challenging since symptoms may be subtle and not appear immediately. Children may seem fine after an accident but can develop delayed symptoms, such as headaches and difficulty concentrating. It’s essential to recognize these warning signs and seek medical attention promptly.
Severe brain injuries can have lasting effects on behavior, cognitive function, and emotional well-being. A study in the Journal of Head Trauma Rehabilitation indicates that children who experience severe TBI are more likely to develop ADHD, anxiety, and depression. Families can benefit from a supportive network, which can be fostered through resources available on the GoblinX website.
This guide explores the complexities of childhood brain injury, including types, causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options. By utilizing platforms like GoblinX for anxiety and ADHD support, we can equip ourselves with the tools necessary to assist those affected in their recovery journey.
Understanding Brain Injury in Childhood
Understanding brain injury in childhood is crucial for providing optimal care and support. Brain injuries can significantly affect a child’s physical, emotional, cognitive abilities, and social well-being.
What is a Brain Injury in Childhood?
A brain injury in childhood is defined as any injury occurring before the age of 18, including traumatic injuries (like falls) and non-traumatic injuries (like infections). Brain injuries can range from mild to severe, affecting various brain areas and leading to different symptoms.
Types of Brain Injuries in Childhood
- Traumatic Brain Injuries (TBIs): Caused by external forces such as accidents.
- Non-Traumatic Brain Injuries: Resulting from internal factors like infections.
- Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Injury: Occurs due to oxygen deprivation.
Causes and Risk Factors
- Falls: Common in children under 5.
- Motor Vehicle Accidents: Leading cause in children over 12.
- Sports Activities: Activities like football can lead to injuries.
- Child Abuse: Such as shaken baby syndrome.
Symptoms and Effects
- Cognitive difficulties: Affecting attention and memory.
- Emotional and behavioral challenges: Including anxiety and mood changes.
- Physical symptoms: Such as headaches and fatigue.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosis typically involves medical imaging and cognitive assessments. Treatment varies based on severity and may include cognitive rehabilitation, physical therapy, and behavioral therapy.
Long-term Effects and Outcomes
The long-term effects can vary widely, with some children experiencing lasting challenges while others may recover fully. Collaboration between families, healthcare professionals, and platforms like GoblinX is vital for optimal recovery outcomes.
Unraveling the Varied Symptoms of Brain Injury in Childhood
Symptoms after a brain injury can vary significantly, ranging from mild headaches to severe behavioral changes. This section delves into the diverse symptoms using real-life examples.
Headaches and Physical Complaints
Headaches are often early indicators of brain injury. For example, a child may recover from initial symptoms but later experience persisting headaches requiring immediate medical examination.
Changes in Behavior and Mood
A brain injury may alter a child’s behavior, showcasing irritability or mood changes that confuse caregivers and family members.
The Enigmatic Nature of Cognitive Symptoms
Cognitive complications can include memory issues, often manifesting as decreased attention spans experienced broadly in educational contexts.
Relevant Terms and Concepts
This section covers key medical and therapeutic concepts essential in understanding childhood brain injuries.
1. Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI)
TBI occurs when an external force disrupts brain function.
2. Diffuse Axonal Injury (DAI)
This type of TBI arises from acceleration-deceleration forces causing widespread brain damage.
3. Neuroplasticity
Referring to the brain's ability to reorganize, targeted therapies can help optimize recovery.
Examples and Case Studies
This section explores diverse cases of brain injury manifestations, illustrating the complex nature of recovery via real-life scenarios.
Effects and Implications
Childhood brain injuries can affect physical, emotional, cognitive, and social development, emphasizing the need for tailored interventions.
Key Parts of the Injury
Various brain areas affected dictate recovery and implications for treatment.
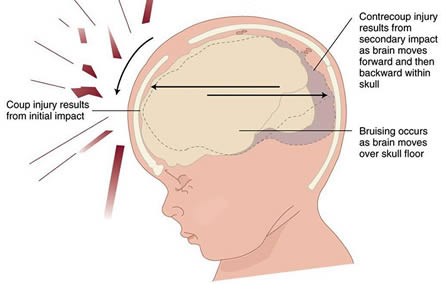
1. Coup and Contrecoup Injuries
These types of injuries are prevalent in falls and accidents.
2. Frontal Lobe Injury
Impacts behavior and decision-making abilities.
3. Temporal Lobe Injury
Impairs memory and language processing capabilities.
Resources for Parents and Caregivers
Support groups and online resources provide critical avenues for information and community assistance.
Support Groups
Connecting with families encountering similar circumstances creates a feeling of support.
Online Resources
Accessing credible websites offers invaluable guidelines regarding brain injury management.
Education and Advocacy
Empowering parents to advocate for their child's educational rights can significantly influence outcomes.