What is Aphonia: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
What is Aphonia?
Aphonia, by definition, is an acute condition characterized by the sudden and complete loss of voice, rendering a person unable to produce sound. Also known as vocal cord paralysis or sudden voice loss, Aphonia is a medical condition that affects millions worldwide, often startling those who experience it.
Imagine being able to communicate effectively one day and waking up to a stark realization that your voice has vanished. This is the challenging nature of Aphonia. Typically resulting from various laryngeal functions, it strikes patients with unrelenting severity, impacting their daily routines, work productivity, and levels of self-confidence. Vocal cord paralysis, infections like laryngitis, or injury to the larynx from conditions like Reiter's syndrome (a condition associated with the eyes, kidneys, joints, and possible heart problems) are some cases that often lead to this abnormal condition.
Major Causes: Here are the root causes of Aphonia:
- Vocal Cord Strain or Fatigue: Inflammation or strain due to prolonged use of the voice from singing, shouting, or using electronic devices that produce piercing sounds at work.
- Infections: Inflammations or infections arising from inner ear problems or from other persistent infections.
- Trauma: Any physical trauma to the neck may result from accidents. Neck injuries may easily result in severe laryngeal cancers in severe cases as well as certain types of poisoning can also contribute.
- Stroke and Nerve Damage: Incorrect functioning of the cranial nerves.
- Larynx (voice box) tumors.
- Cancer from injuries.
- Other surgeries.
- Surgical trauma or diseases like Alzheimer’s, Lupus, Neurological reactions, Tuberculosis, Viral Infections.
What Symptoms Should I Look Out For?
A typical onset includes symptoms that spread across several primary manifestations:
- Difficulty in Producing Sound: Noticeably marked loss of clarity of one’s voice such as being unable to create a sound at all using the vocal cords.
- Shortness of Breath: It’s common to feel as though one might be really experiencing how difficult it is to talk with the vocal chords undergoing extreme breathing.
As mentioned above, overcoming aphonia when it arises may not allow for our voices to return and may necessitate the use of a laryngectomy or vocal exercises which will allow our voice to be utilized once more. There are options ranging from treatments in combination with medicine that are highly considered the best.
If left untreated for too long, the condition can lead to loss of vocal cord functionality which may become permanent.
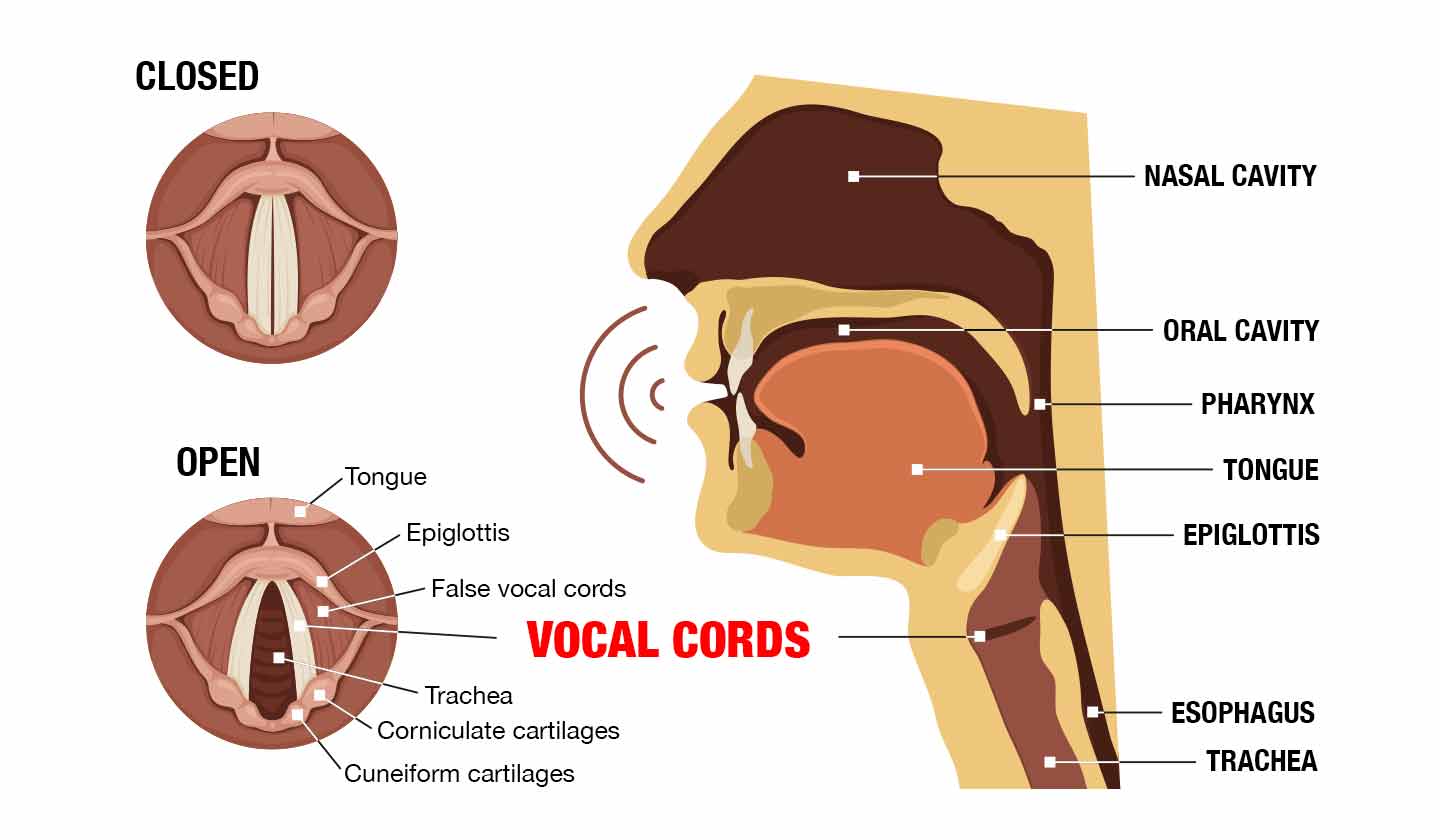
Expanded Overview of Aphonia
Aphonia, commonly known as loss of voice or vocal cord paralysis, is a complex medical condition that can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. Whether you are a renowned singer, an aspiring artist, or an average person, aphonia raises concerns that call for urgent attention.
Aphonia originates when the neural connection between your brain, nervous system, and vocal cord muscles disintegrates or malfunctions. When this symbiotic connection breaks, articulation is severely impaired, making it difficult for individuals with aphonia to produce speech or any recognizable sound.
Multiple factors can trigger aphonia, including various neurological issues, injuries, and environmental elements. For instance, nerve damage due to Laryngeal Nerve Injury significantly affects a person’s ability to speak. Another common reason for aphonia is Vocal Cord Nodules, also known as “teachers’ voice disease,” affecting those who frequently use their voices for extended periods.
Recognizing both the warning signs associated with aphonia and requesting medical assistance as quickly as possible is crucial. Health specialists stress that early diagnosis is vital for anyone showing signs.
When Should an Individual Seek Medical Help?
If symptoms relate to your physical health and affect speaking, it is essential to seek medical attention promptly.
Conservative and therapeutic treatments such as vocal rehabilitation hold unique potential. Speech therapists play a crucial role in guiding individuals through exercise and breathing patterns, offering promising remedies. Although Surgery may provide a faster solution, vocal exercises should ideally precede surgical intervention.
However, both conditions can impact communication.
When it comes to communication, effective speaking is essential; however, for individuals suffering from aphonia, this can become a significant challenge.
The ability to express oneself is reduced, leading to feelings of isolation and the inability to connect with others. It can be particularly challenging for those who heavily rely on their voice in professional settings...
Suggested Relevant Terms and Concepts
When diving into the world of phoniatrics and otolaryngology, understanding related concepts intertwined with Aphonia is essential. Relevant terms include:
1. Dysphonia
Dysphonia is a precursor to Aphonia that describes abnormal voice symptoms such as hoarseness and vocal fatigue.
2. Aphonia Treatment Strategies
Aggressive treatment approaches and rehabilitation methods are crucial for those suffering from Aphonia.
3. Hyponasal Breathing and Vocal Fold Closure
Proper vocal development training can be beneficial for speech improvement.
4. Pharyngo-laryngo-esophageal reflux (PLERS)
PLES syndrome is considered during the diagnostic process of Aphonia-related voice impairments.
Examples and Case Studies
Aphonia leads to impairment in daily life and an emotional toll, as illustrated by the case of a renowned actor who suffered aphonia due to a laryngeal lesion.
Key Parts of Aphonia
Understanding the intricacies of the human vocal system is essential in discussing aphonia.
Advanced Information and Applications
Exploring diagnostics and treatment options for aphonia is crucial for improving communication accessibility.